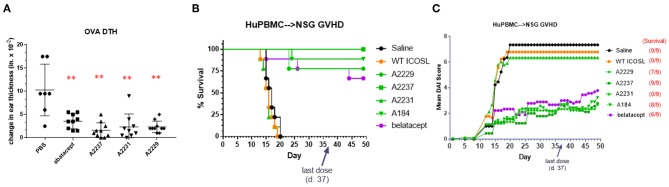
Figure 5.
ICOSL vIgD-Fc suppress immune responses in vivo. (A) A delayed type hypersensitivity (DTH) model was performed by sensitizing mice with OVA and subsequently rechallenging with OVA in the ear pinna. Groups of seven mice treated with either abatacept or ICOSL vIgD-Fc showed significantly less OVA-induced ear swelling as compared to PBS treated animals (**p < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA). Bars shown are the group mean (s.d.). (B,C) An acute model of graft-versus-host-disease (GvHD) was performed by adoptively transferring human PBMC into immunodeficient NSG mice (n = 9/group). (B) High affinity ICOSL vIgD-Fc significantly prolonged survival and (C) significantly reduced mean disease activity index (DAI). Administration of ICOSL vIgD-Fc protected from effects of GvHD at levels comparable to or better than belatacept, but wild-type ICOSL-Fc or lower affinity ICOSL vIgD-Fc were not effective in protecting from GvHD in this model. For (B), by log-rank test, belatacept and high affinity ICOSL vIgD-Fc significantly prolonged survival as compared to saline and WT ICOSL-Fc (p < 0.001) treatments; ICOSL vIgD-Fc A2237 prolongs survival as compared to belatacept (p = 0.065). For (C), by 2-way repeated-measures ANOVA, belatacept and high affinity ICOSL vIgD-Fc significantly reduce DAI scores as compared to saline and wild-type ICOSL-Fc (p < 0.001); ICOSL vIgD-Fc A2229 and A2237 were significantly better at reducing DAI scores than belatacept (p = 0.053 and p = 0.035 for A2229 and A2237, respectively). Both studies were performed at least twice with representative experiments shown here.