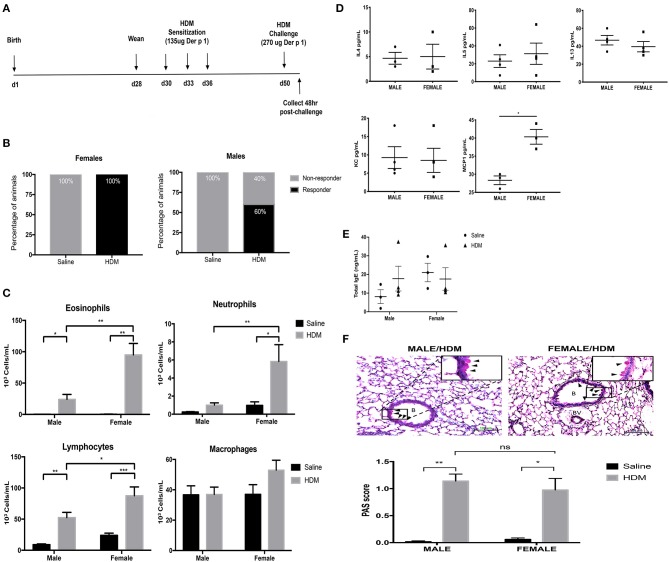
Figure 2.
Characterization of pulmonary immune cells, cytokines, and histopathology in male and female mice. (A) Schematic representation of protocol for induction of allergic asthma in mice. At 28 days of age offspring were weaned, separated by sex, and began intranasal instillation with house dust mite (HDM) or saline. Offspring were sensitized with three intranasal installments of HDM consisting of 135 μg of the major allergen Der p 1 (d30, d33, d36), were challenged with a 2-fold higher dose on d50, and tissue was collected 48 h post-challenge. (B) The percentage of male and female responders to HDM, defined as 10% or greater eosinophil accumulation in the lung; female responders, n = 17/17 (100%), male responders, n = 9/16 (60%). (C) Immune cells were quantified, total eosinophils (*p = 0.002, **p < 0.0001), neutrophils (*p = 0.003, **p = 0.0014), lymphocytes (*p = 0.03, **p = 0.0008, ***p < 0.0001), and alveolar macrophages in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) of male (n = 8–10) and female (n = 7–10) responders. (D) Cytokine and chemokine concentrations in BAL of male and female HDM-treated mice. Interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-5 (IL-5), interleukin-13 (IL-13), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) concentrations are reported as pg/mL in BALF (*p < 0.05, n = 4). (E) Total IgE in serum of male and female offspring treated with saline (circle) and HDM (triangle), with concentrations reported as ng/mL (n = 3–5). (F) Representative light photomicrographs of lung tissue sections from male and female mice stained with Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-hematoxylin. B, bronchiolar airspace; BV, blood vessel; arrows, PAS+ cells; scale bar: 100 μm. Goblet cell hyperplasia was quantified by scoring histological sections based on the percentage of PAS-positive cells lining the bronchoalveolar space: grade 0: <0.5%; grade 1: 0–25%, grade 2: 25–50%, grade 3: 50–75%, grade 4: >75%. The mean PAS scores were compared (*p = 0.0006, **p < 0.0001) (n = 5–7).