Figure 2.
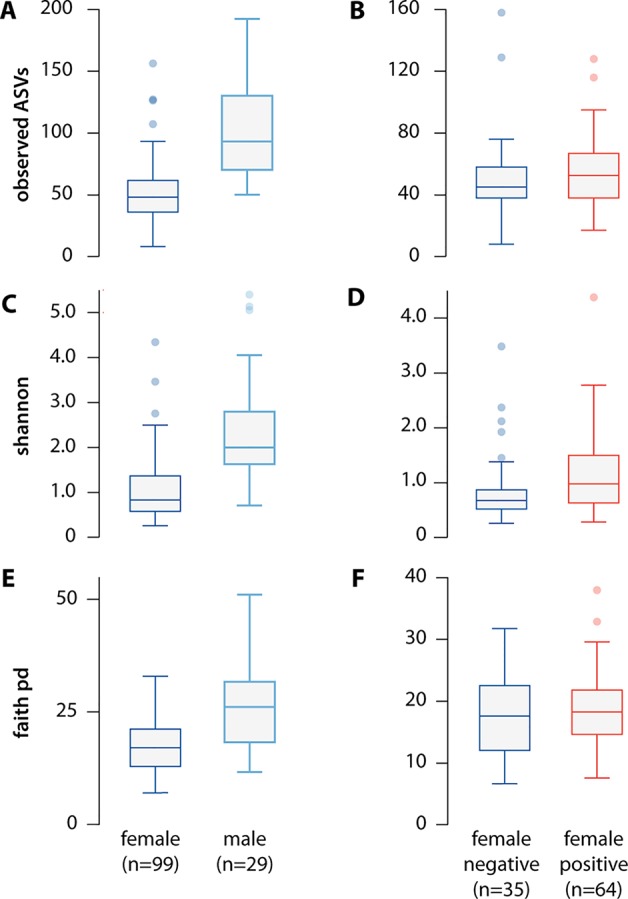
Alpha diversity of the microbiome differs significantly between females and males, but not between B. burgdorferi-infected and uninfected ticks. We measured alpha diversity using three different metrics, including (A) the count of observed ASVs by sex (p = 1.01e-10) and (B) by infection status (p = 0.30), (C) the Shannon index, a non-phylogenetic alpha diversity metric, by sex (p = 6.45e-10), and by (D) infection status (p = 0.02), and (E) Faith's Phylogentic Diversity index, a phylogenetic alpha diversity metric by sex (p = 6.45e-10) and (F) by infection status(p = 0.56). While infection status was significant using the Shannon Index, this difference disappeared after removing B. burgdorferi reads from the analysis (p = 0.58).
