Figure 2.
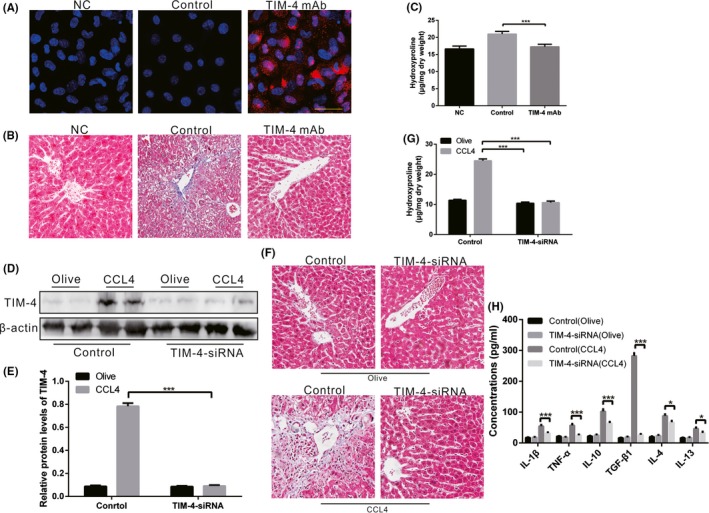
TIM‐4 in KCs is associated with liver fibrosis. A, KCs were isolated from mice with TIM‐4 mAb (red fluorescence label) treatment or control mAb treatment and then examined using laser confocal microscopy to identify the successful blocking of TIM‐4 function (n = 3 mice/ group, Scale bars: 50 μm). Negative control (NC) as negative control without any treatment. B, Liver tissues from TIM‐4 mAb and control mice were processed for Masson's trichrome staining (n = 3 mice/ group, magnification, ×400). NC as negative control without any treatment. C, Hydroxyproline of livers removed from olive‐induced and CCL4‐induced mice with or without TIM‐4 mAb treatment (n = 3 mice/ group). D, E, Mannose‐conjugated polymers were used to deliver TIM‐4 siRNA or its scrambled control siRNA in vivo, and the expression levels of TIM‐4 in olive‐induced and CCL4‐induced liver were assessed using immunoblot and quantitative analysis (n = 3 mice/ group). F, Liver tissues from each group processed for Masson's trichrome staining (n = 3 mice/ group, magnification, x400). G, Hydroxyproline of livers removed from olive‐induced and CCL4‐induced mice with or without TIM‐4 interference (n = 3 mice/ group). H, Inflammatory factors in livers were measured by enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (n = 3 mice/ group). ***P < .0001. Values represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments
