Figure 4.
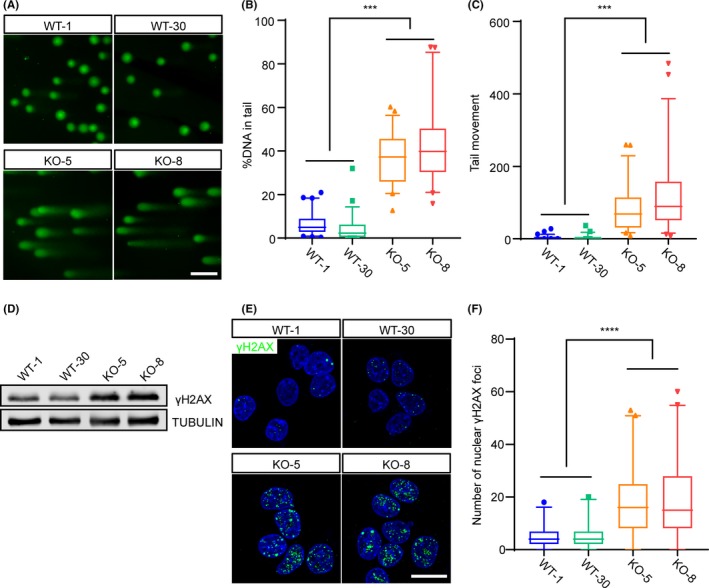
Rbm14 knockout causes DNA damage in mouse embryonic stem cells. A‐C, Comet assay reveals severe DNA damage in the Rbm14 knockout embryonic stem cells (ESCs). Genomic DNA was stained with SYBR Gold and imaged after single cell electrophoresis (A). Scale bar, 50 μm. Quantification for the percent of DNA in the comet tail (B). Quantification for the length of the tail movement (C). Data are shown as mean ± SEM (for WT‐1, n = 69; for WT‐30, n = 51; for KO‐5, n = 51 and for KO‐8, n = 45.) ***P < .001, Student's t‐test. D, Western blot shows elevated γH2AX protein level in the Rbm14 knockout ESCs. E, Representative immunofluorescent images of wild type and knockout ESCs for the DNA damage marker γH2AX (green). The nuclei were counterstained with 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI) and are shown in blue. Increased γH2AX foci are detected in Rbm14 knockout ESCs. Scale bar, 10 μm. F, Quantification of the γH2AX foci in the immunofluorescent staining in (D). More than 50 cells were analysed in each group. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (for WT‐1, n = 189; for WT‐30, n = 190; for KO‐5, n = 211 and for KO‐8, n = 208.) **P < .01, Student's t‐test
