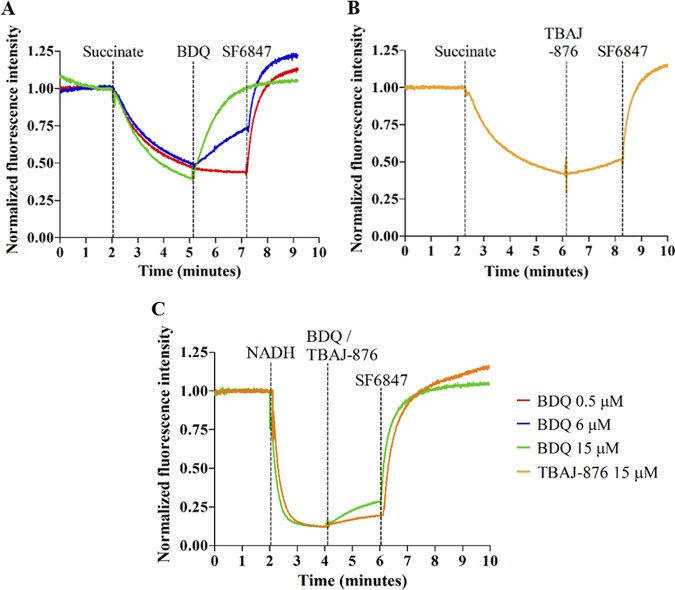
FIG 2.
Effects of BDQ and TBAJ-876 on the transmembrane pH gradient of inverted vesicles prepared from M. smegmatis plasma membrane. Shown are the effects of 0.5, 6, and 15 μM BDQ (A and C) or 15 μM TBAJ-876 (B and C) on the quenching of fluorescence of the pH-sensitive fluorophore ACMA. At the beginning of the experiments, 0.5 mM succinate (A and B) or 2 mM NADH (C) was added as an electron donor to the vesicle samples. The inverted vesicles oxidized succinate/NADH and pumped protons to generate the transmembrane pH gradient, visualized as quenching of fluorescence; 1 μM uncoupler SF6847 was added at the end of each experiment as a positive control to collapse the transmembrane pH gradient. The vertical dotted lines indicate the time points at which succinate, NADH, BDQ, TBAJ-876, or SF6847 was added. The experiments were carried out twice independently, showing the same result. Data from a representative replicate are shown. The graphs were generated using GraphPad Prism 5 software. The MIC90s for BDQ and TBAJ-876 against M. smegmatis are 100 nM and 6.3 nM, respectively, as described in reference 15.