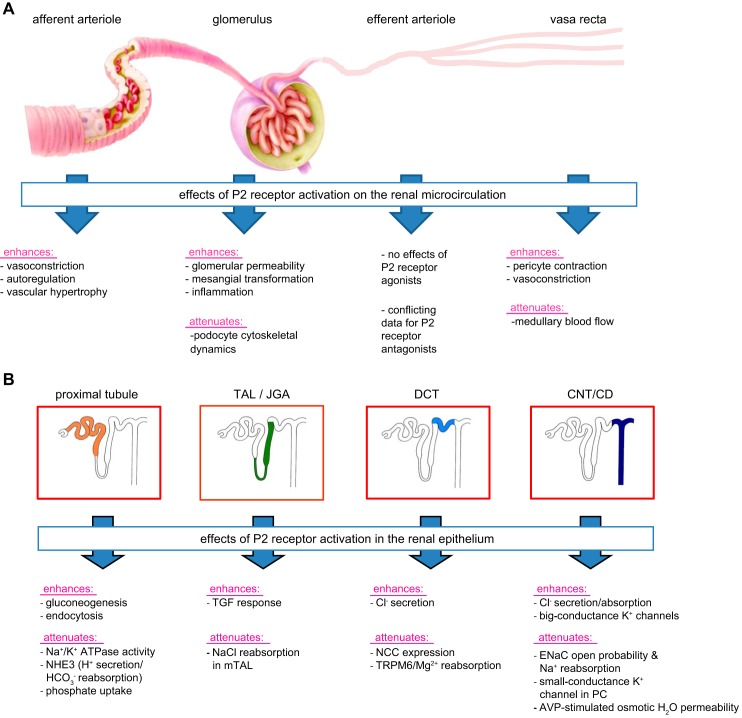
FIGURE 3.
Some examples of P2 receptor-mediated effects of ATP on the vascular segments (A) and the nephron and collecting duct system (B). A: P2 receptor activation induces distinct effects on the renal vasculature, including constriction of the afferent arteriole and vasa recta, with the former contributing to renal autoregulation of glomerular filtration rate and renal blood flow. B: P2 receptor activation affects multiple transport processes along the nephron and collecting duct system, including the inhibition of Na+ reabsorption in multiple segments and of water reabsorption in the connectin tubule (CNT)/cortical collecting duct (CCD). TAL, thick ascending limb; JGA, juxtaglomerular apparatus; DCT, distal convoluted tubule; TGF, tubuloglomerular feedback; ENaC, epithelial sodium channel; PC, principal cell; AVP, arginine vasopressin. See text for details.