Fig. 5.
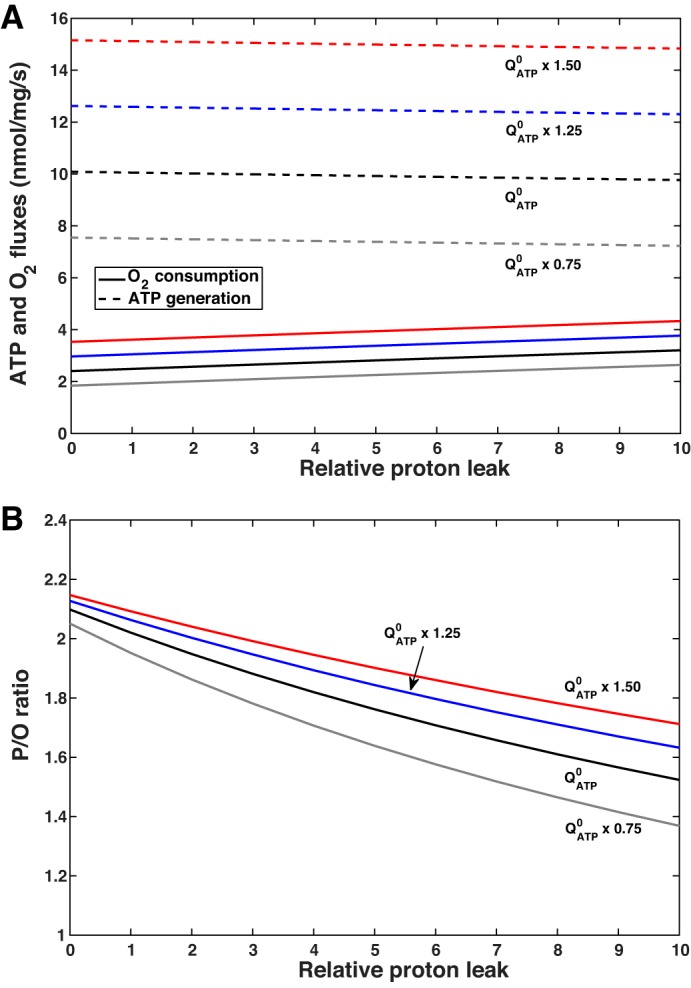
Predicted effect of proton leak permeability on ATP formation by F0F1-ATP synthase and O2 consumption (A) and P/O (amount of ATP produced by F0F1-ATP synthase per oxygen atom reduced by the respiratory chain; B) for different values of ATP hydrolysis (QATP). K+ leak permeability is kept constant. denotes the baseline value of QATP.
