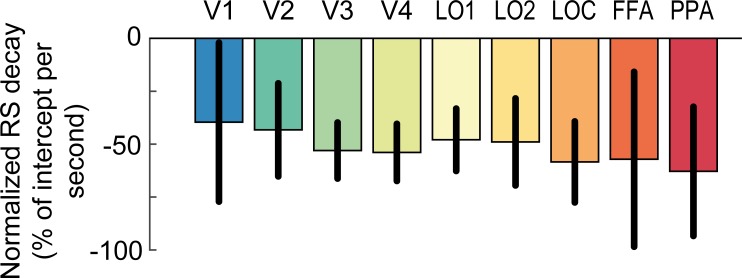
Fig. 4.
Decay of repetition suppression normalized to its initial magnitude. The slope parameter estimates of the linear model fits to repetition suppression (RS) scores (see Fig. 3C) are normalized by the group mean intercept estimates for each region (see Fig. 3B), respectively. The normalized slope parameter estimate accounts for differences in slope due to differences in the initial magnitude of RS across visual areas. RS decays similarly across posterior and anterior visual areas and is reduced to approximately half of its initial magnitude after 1 s. Error bars denote 95% within-subject confidence intervals. FFA, fusiform face area; PPA, parahippocampal place area; V1–V4, visual areas 1–4; LOC, lateral occipital complex; LO1 and LO2, lateral occipital areas 1 and 2.