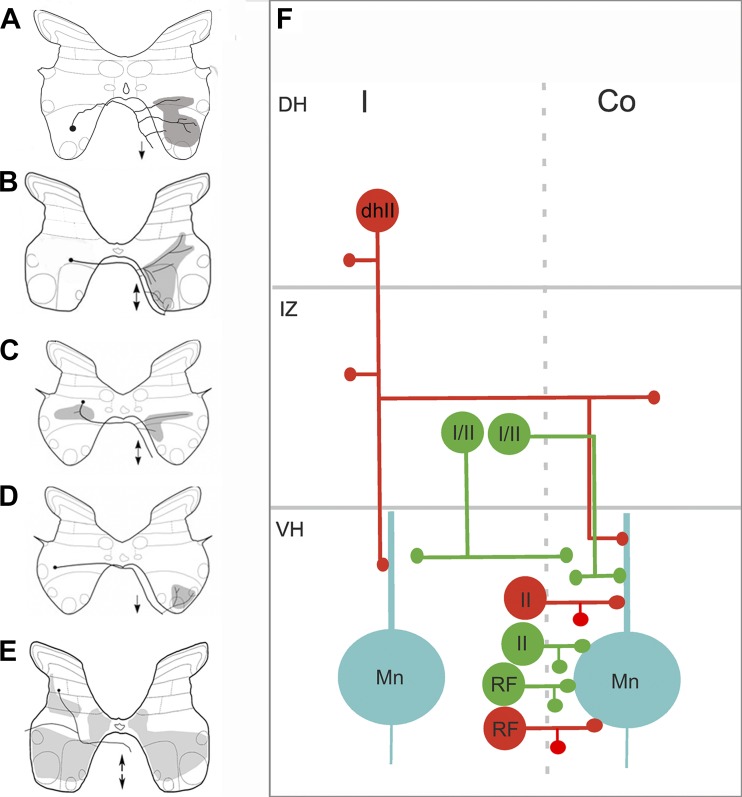
Fig. 6.
Projections of identified commissural interneurons (CINs) in cat midlumbar segments. A–E: cartoons illustrating typical projections of cells [adapted from Bannatyne et al. 2003, 2006 (© 2006 Society for Neuroscience); 2009; Jankowska et al. 2009]. The black dot represents the location of the cell body; black lines show axonal projections, and shaded gray areas show areas of the gray matter innervated by axon terminals. Double-headed arrows in B, C, and E indicate axons that bifurcate and ascend and descend in the contralateral ventral funiculus. Single-headed arrows in A and D indicate descending axons. A: lamina VIII cell monosynaptically activated by reticulospinal fibers. B: a group II-activated lamina VIII cell. C: a group I/II cell in the intermediate gray matter with bilateral projections. D: a group I/II cell with a contralateral projection. E: a dorsal horn group II activated cell with extensive ipsilateral and contralateral projections. F: a schematic diagram showing these projections. Inhibitory cells are in red and excitatory cells are in green. Co, contralateral; DH, dorsal horn; dhII, dorsal horn group II activated cell; I, ipsilateral; I/II, cells in the intermediate gray activated by group I and II afferent fibers; II, lamina VIII group II activated cell; IZ, intermediate zone; Mn, motoneuron; RF, lamina VIII cell activated by reticulospinal axons; VH, ventral horn.