Fig. 2.
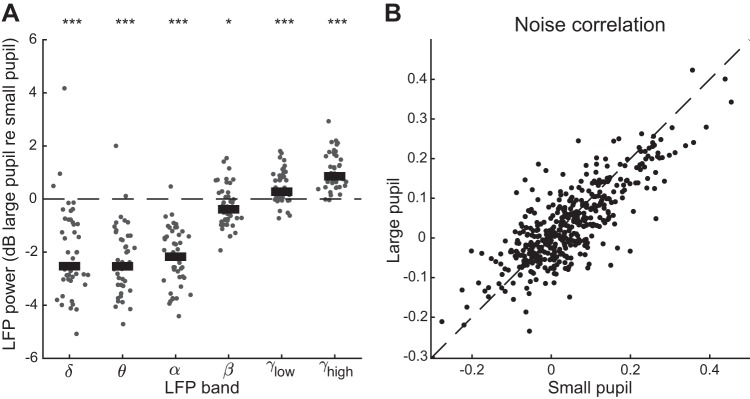
Dilated pupil is associated with neural desynchronization. A: log ratio change (dB) in local field potential (LFP) power between recording segments with large and small pupil (n = 46 recordings). Thick bar indicates population median. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001, rank-sum test on hypothesis that median is equal to 0. Putative sleep states (see Fig. 8) have been excluded from the comparison. B: change in noise correlation across large- and small-pupil trials [n = 429 neuronal pairs; mean noise correlation = 0.03 (large pupil), 0.04 (small pupil); P = 1.1e-03, paired t test]. Trials are classified as “large pupil” and “small pupil” based on whether the mean pupil size preceding the vocalization is greater or less than the median pupil size during the recording.