Fig. 3.
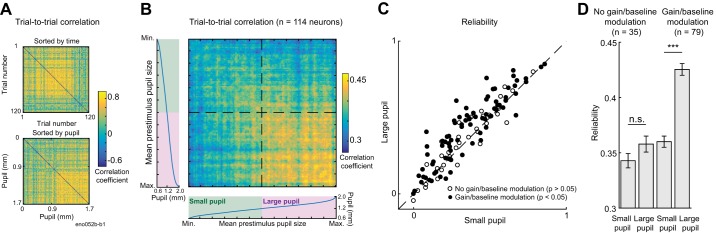
Reliability of neural response to sound increases when pupil is dilated. A: correlation between time-varying activity across trials evoked by 1 ferret vocalization in 1 neuron, sorted by trial order (top) and mean pupil size before stimulus onset (bottom). B: mean trial-to-trial correlation for all neural responses to ferret vocalizations. Heat map was constructed by computing the average correlation matrix sorted by pupil size across all neurons (n = 114). For display, the correlation of each trial with itself was replaced by the mean correlation for the 2 trials with the most similar pupil size before averaging. Marginal plots indicate the mean pupil size in each trial, across all neurons (Max., maximum; Min., minimum). Dashed line indicates median pupil size. C: comparison of reliability (mean trial-to-trial correlation) for each neuron’s response to vocalizations for small vs. large pupil (n = 114; P = 5e-8, paired t test). Trials are classified as “large pupil” and “small pupil” based on whether the mean pupil size preceding the vocalization is greater or less than the median pupil size during the recording. Closed circles indicate cells with a significant fit under a second-order baseline-gain regression model (n = 79; P < 0.05, permutation test; P = 5e-8, paired t test). D: mean (±SE) reliability in each condition for subpopulations of cells that do or do not show an effect of pupil-associated state under the regression model.***P < 0.001, paired t test; n.s., not significant.