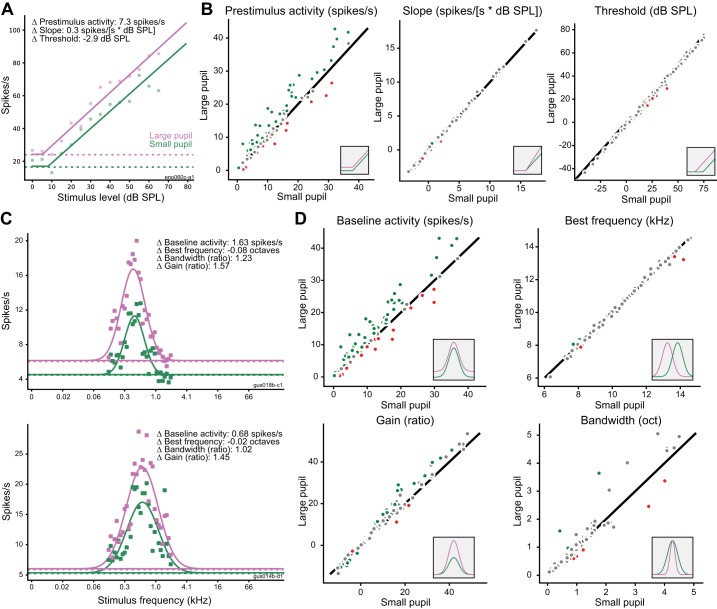
Fig. 7.
Effects of pupil-related state on frequency and level tuning. A: example of hinge function fit to neural response at characteristic frequency for large-pupil (purple) and small-pupil (green) conditions. Dashed lines indicate prestimulus firing rate in each condition. B: comparison of each parameter of rate-level function between pupil conditions (large pupil vs. small pupil) for all neurons (n = 114). Insets illustrate effect of changing each parameter fit. Green and red circles indicate neurons with a significant change in the tuning parameter (as defined by the 90% credible interval for difference between conditions not bracketing 0). Gray dots indicate neurons with changes that were not significant at the single-cell level. C: examples of Gaussian functions fit to neural responses at best level for large-pupil (purple) and small-pupil conditions (green). D: comparison of each parameter of the frequency-tuning curve across pupil conditions for all neurons (n = 114). Insets and color coding as in B. oct, Octaves.