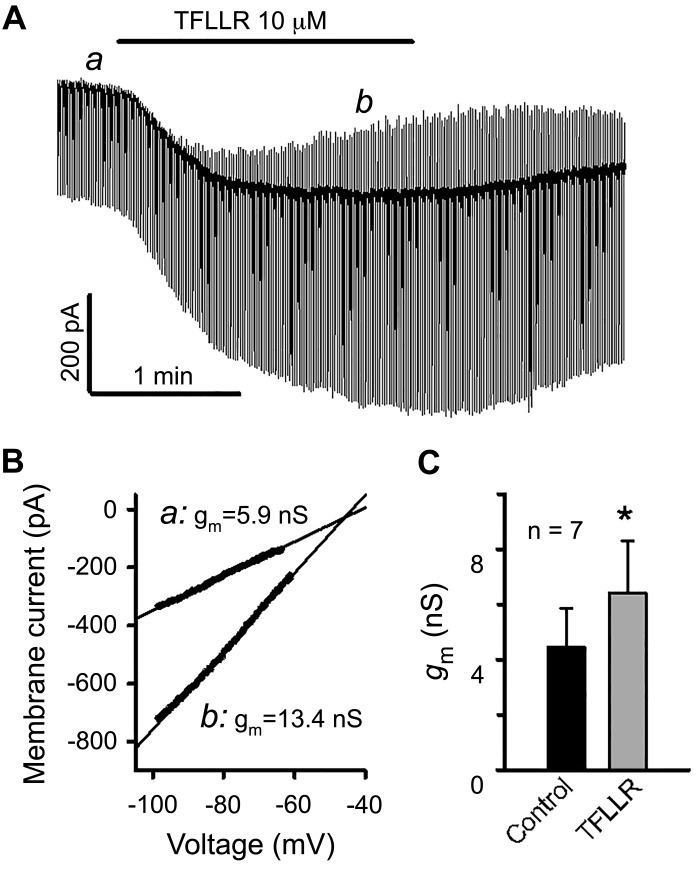
Fig. 4.
Effect of protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1) activation on membrane current and membrane conductance. A: continuous display of membrane current elicited by repetitive ramp voltage commands (from −100 to −50 mV for 300 ms, 1 Hz) from a holding potential of −70 mV before and after bath application of TFLLR. B: current-voltage plots for the linear portion of voltage ramp-elicited currents taken at indicated time points (a and b in A). Solid lines represent the fits of currents to a linear function. The slope of the curves gave an estimate of membrane conductance (gm). In this neuron, PAR1 activation increased gm, and the TFLLR-induced current reversed at −45.8 mV. C: averaged gm increase caused by PAR-1 activation. *P < 0.05 (paired t test).