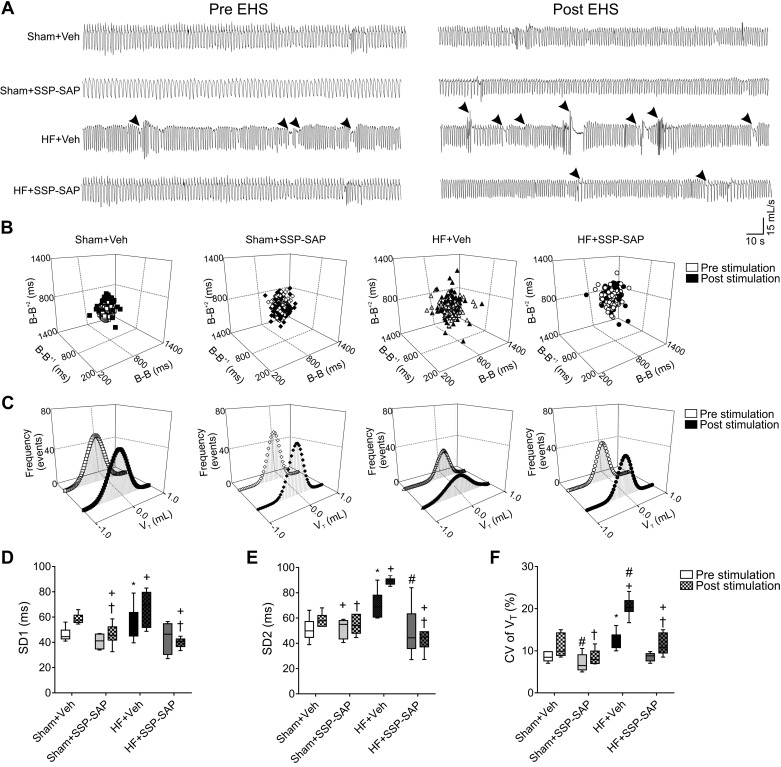
Fig. 4.
Selective ablation of retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN) chemosensory neurons prevents ventilatory disturbances elicited by episodic hypercapnic stimulation. A: representative traces of ventilation during pre- and post-episodic hypercapnic stimulation (EHS) phases. Arrows point to disturbances in breathing patterns such as apneas/hypopneas. B and C: representative Poincaré plots and histograms during pre- and post-EHS phases. D and E: summary data of short-term (SD1) (D) and long-term variability (SD2) (E), and coefficient of variation (CV) of tidal volume (VT) (F) during pre- and post-EHS phases. Substance P-conjugated saporin (SSP-SAP) toxin injection in the RTN diminished breath-to-breath and VT amplitude variability in the post-EHS phase in heart failure (HF) rats. Box and whiskers represent median ± range. Two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc tests; n = 6 rats per group. *P < 0.05 vs. Sham+Veh Pre; #P < 0.05 vs. HF+Veh Pre; +P < 0.05 vs. Sham+Veh Post; †P < 0.05 vs. HF+Veh Post.