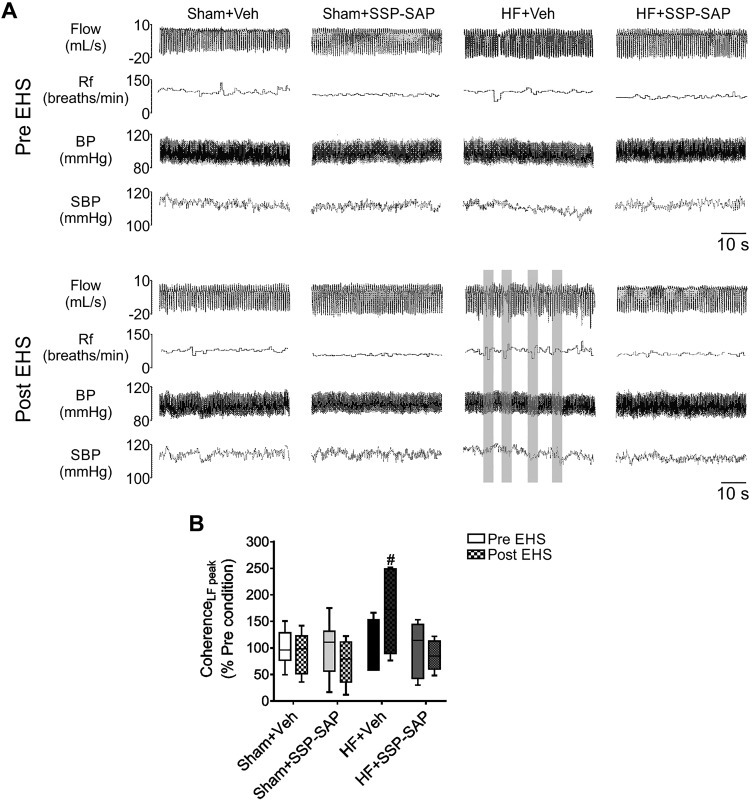
Fig. 7.
Episodic hypercapnic stimulation-induced respiratory-cardiovascular coupling in heart failure depends on intact retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN) chemoreceptor neurons. A: representative traces of respiratory flow, respiratory frequency (Rf), blood pressure (BP), and systolic blood pressure (SBP) in 1 rat per group during pre- and post-episodic hypercapnic stimulation (EHS) phase. Segments where coupling between ventilatory and cardiovascular signals was observed are highlighted (gray). B: summary data of coherence analysis. Note that following EHS, heart failure (HF) rats displayed an increased coherence between tidal volume (VT) oscillation and SBP, and this was blunted in HF rats treated with substance P-conjugated saporin (SSP-SAP) toxin. Box and whiskers represent median ± range. Two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc analysis; n = 6 rats per group. #P < 0.05 vs. HF+Veh Pre-EHS. LF, low frequency.