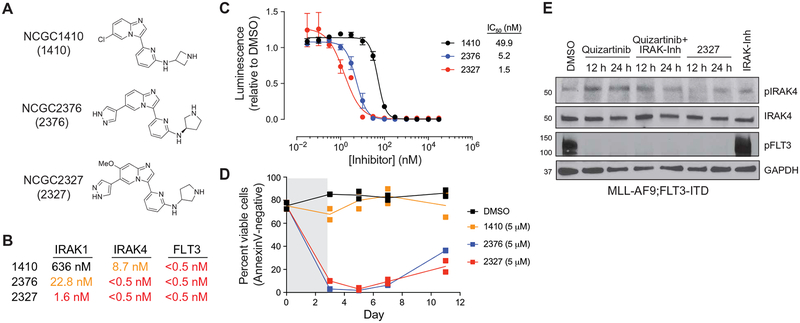
Fig. 3. Structure activity relationship of small-molecule inhibitors reveals the importance of targeting IRAK1/4 and FLT3 in FLT3+ AML.
(A) Chemical structures of NCGC1410, NCGC2376, and NCGC2327. (B) The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) for NCGC1410, NCGC2376, and NCGC2327 on IRAK1, IRAK4, and FLT3 activity (Reaction Biology). (C) Metabolic activity of MLL-AF9;FLT3-ITD cells treated with NCGC1410, NCGC2376, or NCGC2327 for 72 hours as measured by CellTiter-Glo. Values are expressed as means ± SEM from three biological replicates. (D) Viability of MLL-AF9;FLT3-ITD cells treated for 3 days with DMSO (vehicle control), NCGC1410, NCGC2376, or NCGC2327. Individual data points are shown along with the mean from two biological replicates. (E) Immunoblotting of MLL-AF9;FLT3-ITD cells treated with quizartinib (50 nM), quizartinib and IRAK-Inh (10 μM), NCGC2327 (50 nM), or IRAK-Inh.