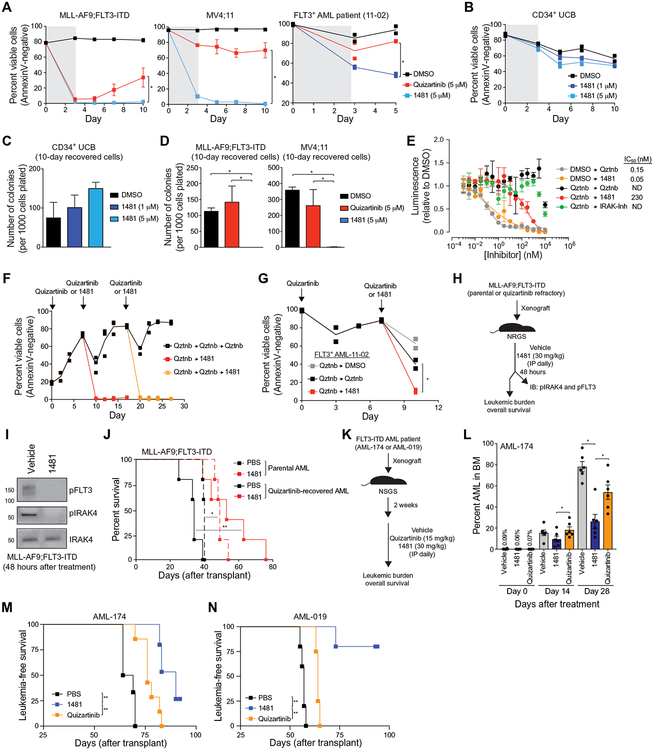
Fig. 6. NCGC1481 prevents adaptive resistance in FLT3-ITD AML cells in vitro and in vivo.
(A) MLL-AF9;FLT3-ITD, MV4;11, or FLT3-ITD AML patient-derived cells were cultured with quizartinib or NCGC1481 for 3 days and replated in fresh medium, and cell viability was measured by AnnexinV staining. Values are expressed as means ± SEM from three to four biological replicates for cell lines and two replicates for the patient sample. *P < 0.05 (unpaired, two-tailed t test). (B) Healthy human CD34+ umbilical cord blood (UCB) cells were treated with 1481 (1 or 5 μM) for 3 days and replated in fresh medium. Cell viability was measured by AnnexinV staining. Individual data points are shown along with the mean from two biological replicates. (C) After 10 days in liquid culture [from (B)], the remaining viable CD34+ cells were plated in methylcellulose, and colony formation was determined after 14 days. Values are expressed as means ± SEM from four biological replicates. (D) After 10 days in liquid culture [from (A)], the remaining viable cells were plated in methylcellulose, and colony formation was determined after 7 days. Values are expressed as means ± SEM from four biological replicates. *P < 0.05 (unpaired, two-tailed t test). (E) MV4;11 cells were cultured with quizartinib (5 μM) for 3 days and replated in fresh medium, and cell proliferation was determined after treatment with the indicated concentration of NCGC1481 or quizartinib (Qztnb) for 72 hours. Values are expressed as means ± SEM from three biological replicates. (F) MLL-AF9;FLT3-ITD cells were cultured with quizartinib (5 μM) for 3 days, plated in fresh medium (days 0 and 7), and then replated in medium containing quizartinib (5 μM) or NCGC1481 (5 μM) at days 7 and 17. Cell viability was measured by AnnexinV staining. Individual data points are shown along with the mean from two to three biological replicates. (G) FLT3-ITD AML patient-derived cells were cultured with quizartinib (5 μM) for 3 days, plated in fresh medium, and then replated in medium containing DMSO, quizartinib (5 μM), or NCGC1481 (5 μM) at day 7. Cell viability was measured by AnnexinV staining. Individual data points are shown along with the mean from two biological replicates. (H) Overview of experimental design of xenograft studies. Parental or quizartinib refractory [from (E)] MLL-AF9;FLT3-ITD cells were intravenously injected into NRGS mice. On day 10 after transplant, the mice were intraperitoneally (IP) treated with NCGC1481 (30 mg/kg) or vehicle control daily (n = 5 mice per condition). (I) After 48 hours of treatment with NCGC1481, MLL-AF9;FLT3-ITD (GFP+) cells were isolated from the BM for immunoblot (IB) analysis. (J) Disease-free survival of NRGS mice xenografted with parental or quizartinib refractory MLL-AF9;FLT3-ITD cells and treated with NCGC1481 or vehicle (n = 5 mice per condition). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 (Mantel-Cox test). (K) Overview of experimental design of xenograft studies using FLT3-ITD AML cells obtained from a patient (FLT3+ AML-174). FLT3-ITD AML cells were intravenously injected into NSGS mice. Two weeks after transplant, mice were treated with vehicle control, quizartinib (15 mg/kg), or NCGC1481 (30 mg/kg) intraperitoneally daily. (L) BM aspirates were analyzed for leukemic burden on days 0, 14, and 28 after treatment (n = 6 mice per condition). Values are expressed as means ± SEM from six individual mice. *P < 0.05 (unpaired, two-tailed t test). (M) Leukemia-free survival of NRGS mice xenografted with AML-174 patient cells and treated with quizartinib, NCGC1481, or vehicle (n = 5 to 7 mice per group). **P < 0.005 (Mantel-Cox test). (N) Leukemia-free survival of NRGS mice xenografted with AML-019 patient cells and treated with quizartinib, NCGC1481, or vehicle (n = 4 to 5 mice per group). **P < 0.005 (Mantel-Cox test).