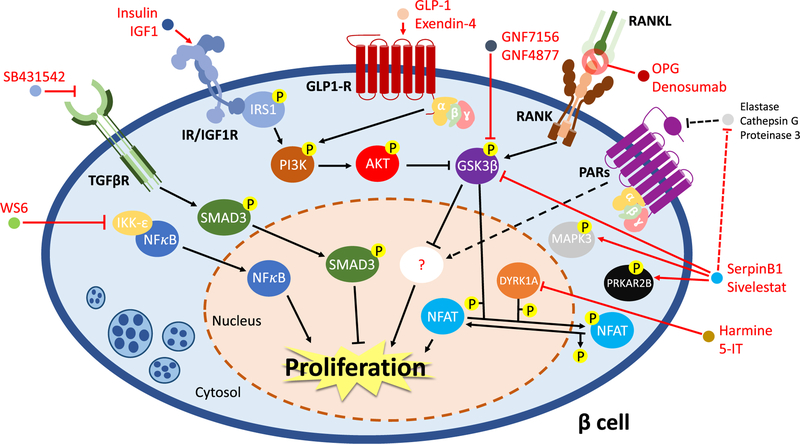
Fig. 2.
Molecular mechanism(s) regulating human β-cell proliferation. The nuclear factor kappa-B (NFκB) is retained in the cytosol and its function is repressed by inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit epsilon (IKK-ε). WS6 blocks IKK-ε inhibition on NFκB, which can translocate into the nucleus and promote cell growth. TGF-β pathway impacts β-cell proliferation via the activation of SMAD3. SB431542, a TGF-βR inhibitor, promotes cell growth by preventing SMAD3 activation. Insulin receptor (IR)/insulin-like growth factor (IGF1R) and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) signaling pathways trigger β-cell regeneration via modulating PI3K-AKT axis, resulting in the inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β) activity. In addition, inactivation of GSK3β is also obtained by treatments with GNF7156 and GNF4877, GSK3β inhibitors, or osteoprotegerin (OPG) or denosumab. In particular, OPG and denosumab act as mimics of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL), preventing its interaction with receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B (RANK) and avoiding the activation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Moreover, the hepatokine SerpinB1 and the elastase inhibitor sivelestat stimulate human β-cell proliferation increasing the phosphorylation levels of mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 (MAPK3), protein kinase cAMP-dependent type II regulatory subunit beta (PRKAR2B) and GSK3β, likely following inhibition of proteases as elastase, cathepsin G, or proteinase 3. These effects might involve the protease-activated receptor (PARs) signaling, but such a hypothesis requires further investigations (dotted lines and arrows). The dual-specificity tyrosine-regulated kinase-1a (DYRK1A) represses β-cell proliferation by phosphorylating and retaining into the cytosol the nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT). The inhibition of DYRK1A, using small molecules as harmine or 5-iodotubercidin (5-IT), results in the decrease of the phosphorylation state of NFAT, which translocate into the nucleus and activate the mitogenic pathways in human β-cells