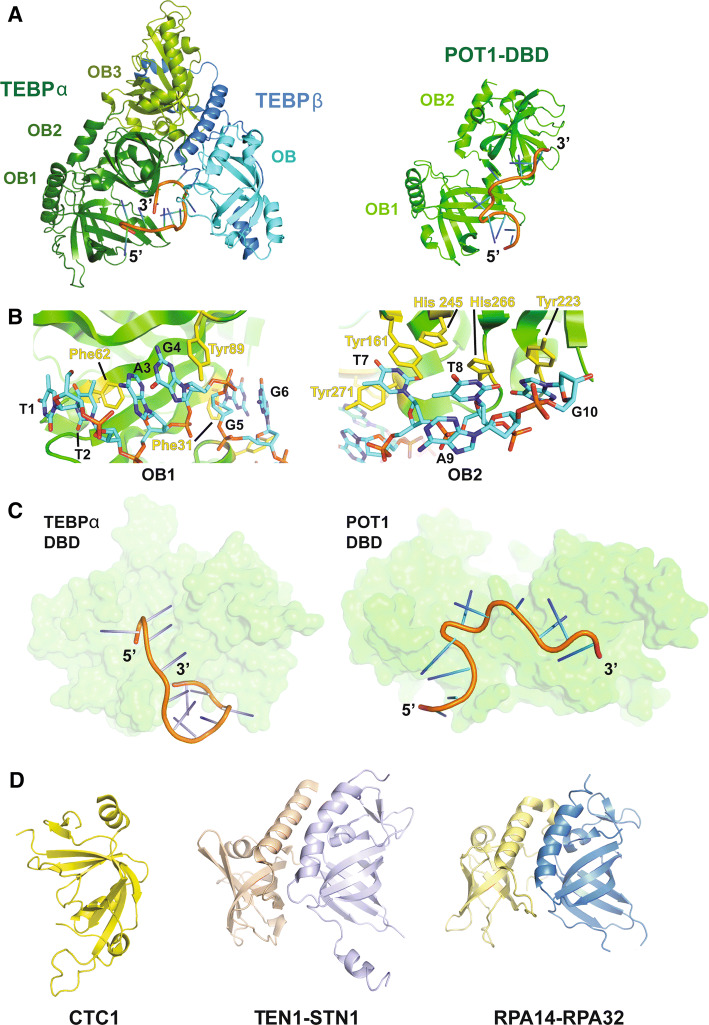
Fig. 3.
Structural basis for single-stranded chromosome end protection. a Left: the structure of TEBP-α-β in complex with ss DNA (5′-d(GGGTTTTGGGG)-3′) (PDB ID: 2I0Q). The DBD and TEBP-β-binding domain of TEBP-α are shown in forest green and split pea green, respectively. The TEBP-α binding domain and OB domain of TEBP-β are shown in blue and cyan, respectively. Right: the human POT1 DNA-binding domain (DBD; PDB ID: 1XJV) shown in green in complex with telomeric DNA [5′-d(TTAGGGTTAG)-3′]. The DNA is shown in cartoon representation. b Views showing stacking interactions between the two OB domains of hPOT1 DBD and telomeric DNA. The stacking protein and DNA residues are shown in stick representation. c Views of TEBP-α DBD in complex with telomeric DNA (left; from the TEBP-α–β–DNA structure) and POT1 DBD in complex with telomeric DNA (right) to highlight the different tracks adopted by the DNA molecules in the two structures. The proteins are shown in surface representation and the DNA is rendered in cartoon representation. d Left: the central domain of human CTC1 (PDB ID: 5W2L). Center: high-resolution structure of the human STN1–TEN1 complex (PDB ID: 4JOI). STN1 is shown in wheat and TEN1 is shown in pale violet. Right: heterodimeric structure of RPA14 (yellow) and RPA 32 (blue) of the trimeric RPA complex (PDB ID: 1QUQ)