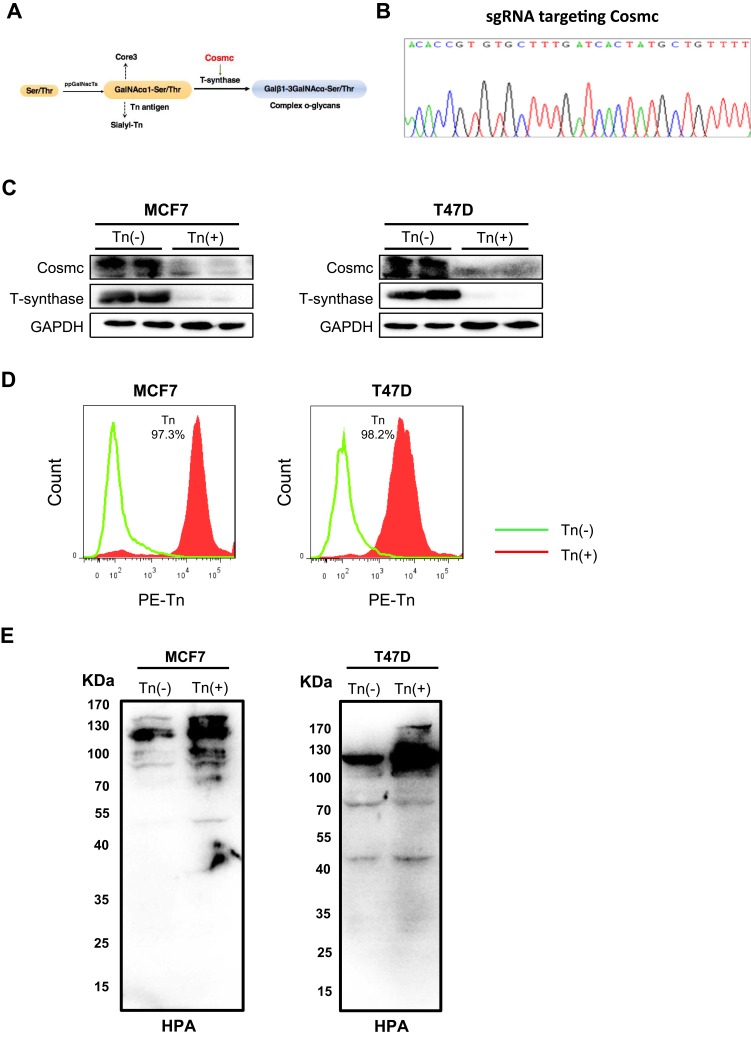
Figure 1.
Forced depletion of Cosmc results in Tn antigen expression in breast cancer cells. (A) Schematic depiction of the biosynthesis of mucin-type O-glycans showing the key regulatory role of Cosmc in the process of O-glycosylation. Deletion of Cosmc results in inactive T-synthase and expression of Tn antigen. (B) One pair of single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) was designed to specifically target the Cosmc gene. (C) The knockout of the Cosmc chaperone and the degradation of T-synthase were confirmed by Western blotting in two breast cancer cells. (D) Flow cytometry analysis of Tn antigen expression with anti-Tn antibody. The percentages of Tn-positive cells were 97.1% and 98.3% in Cosmc-deficiency MCF7 and T47D cells, respectively. (E) Western blot analysis showed a strong expression of Tn antigen in MCF7 and T47D Tn-positive cells compared to the control cells. The membrane was blotted with HPR-labeled HPA.