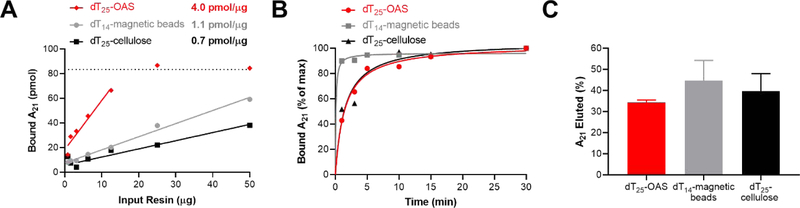
Figure 1. Poly-dA binding properties of dT-resins.
A: The binding capacity of each resin was measured using a poly-deoxyadenosine binding assay. 83 pmol dA21 oligo was incubated with a 1–50 μg of dT-resin for 1 h and the A260 of the supernatant used to calculate pmol of bound dA21. The slope of the curve at non-saturating conditions describes the binding capacity in pmol dA21/μg resin. The dotted line represents the A21 oligo input. B: Time course of poly-deoxyadenosine binding assay with 20.8 μg dT25-OAS, 76.8 μg dT14-magnetic beads and 125.8 μg dT25-cellulose. The time-series data was normalized to the mass of poly-dA bound at 30 min and fit using a one-site specific binding model in GraphPad Prism (solid lines). C: The elution efficiency was measured by treating 50 μg dA21-loaded resin with 1 mM NaOH and calculating the % elution based on the mass of input dA21.