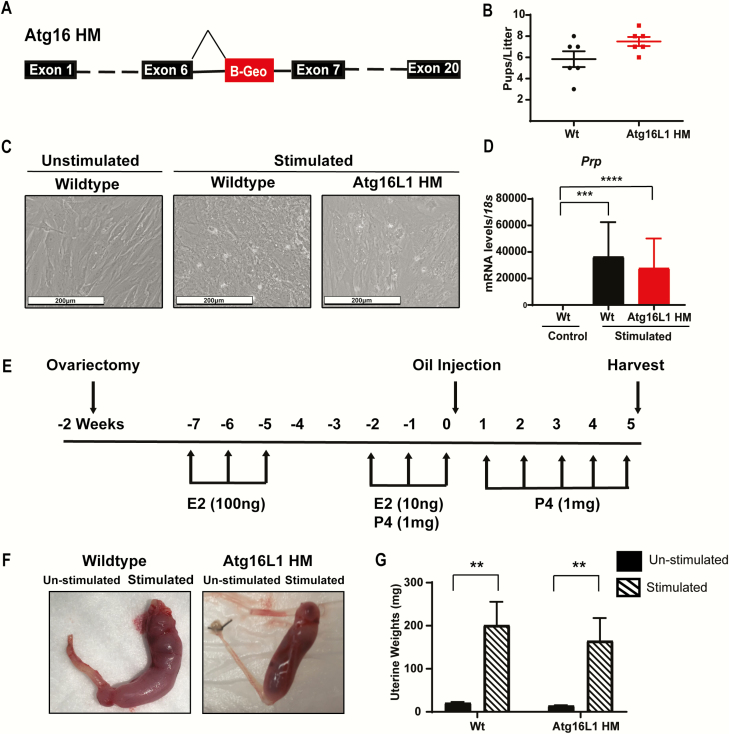
Figure 1.
Atg16L1 HM mice are fertile and maintain the ability to decidualize. A) Diagram of the Atg16L1 HM mutation. B) Live birth rate of Wildtype (Wt) and Atg16L1 HM mice reveals that Atg16L1 HM mice are fertile. C) In vitro hormonal decidualization of endometrial stromal cells from Wt and Atg16L1 HM mice and D) Expression of the decidualization marker Prp show proper decidualization in Atg16L1 mice (n = 3 Wt, 5 Atg16L1 HM). E) Diagram of in vivo artificial decidualization method. F) Uterine horns of Wt and Atg16L1 HM mice and G) Resulting wet weights demonstrate Atg16L1 HM mice maintain the ability to decidualize in vivo (n = 10 Wt, 12 Atg16L1 HM). E2-estrogen, P4-progesterone; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. ****P < 0.0001.