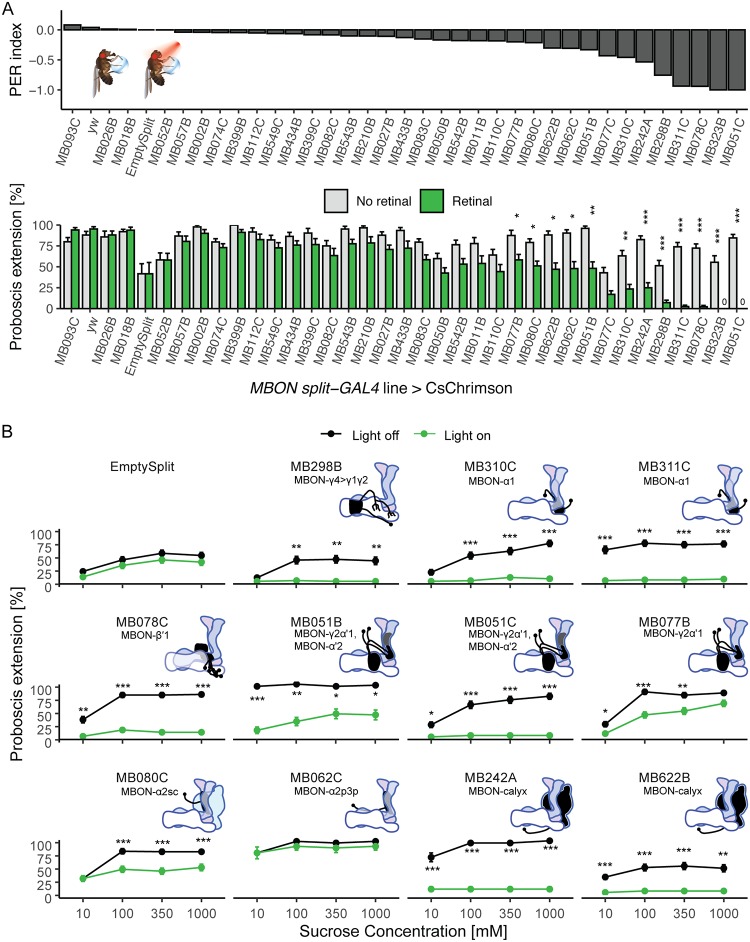
Fig 1. Identification of MBONs that suppress proboscis extension to sucrose.
A) Behavioral screen for flies that change their rate of proboscis extension when MBONs are activated. MBON split-Gal4 lines were crossed to UAS-CsChrimson for light induced activation and tested for proboscis extension to simultaneous red light and sucrose presentation to the tarsi. Extension rates were compared between flies fed retinal and those not. (n = 20–48 flies per line). Inset: Illustration of the PER assay. Top: results of the screen, ordered by PER index to reveal Gal4 lines with the greatest change in PER upon MBON activation. PER index = (Retinal–no retinal) / (Retinal + no retinal). Bottom: Same data ordered as in top, shown as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using Wilcoxon Rank Sum tests (retinal versus no retinal) with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons, *p<0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Green bars represent flies fed retinal. Grey bars represent flies not fed retinal. B) Retest of candidates causing the greatest PER suppression upon MBON activation with CsChrimson. Values represent mean (± SEM) fraction of flies presented with sucrose (black lines) and flies presented with sucrose and red light (green lines) exhibiting PER to the indicated concentrations of sucrose (n = 26–57). Asterisks denote statistically significant differences between flies in light and dark conditions. Statistical significance was calculated using a two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction, where *p<0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Insets show MB dendritic arbors of each MBON class.