Figure 5.
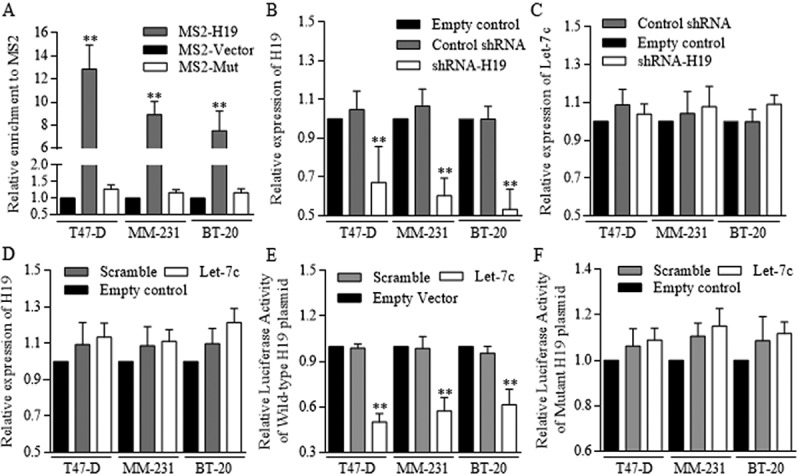
H19 inhibited the Let-7c functions as its competitive sponge molecular.
RNA immunoprecipitation was performed to identify the potential binding site between H19 and Let-7c. (a) Let-7c specific MS2 at the H19 targeted region was effectively enriched in groups of three cell lines, comparing to empty MS2 and the MS2 with mutant H19 region. ShRNA conducted H19 inhibition was successfully achieved (b) however, the inhibition did not influence Let-7c level effectively (c) (d) Let-7c exerted no significant repression on H19 expression level. The potential binding site between H19 and Let-7 was explored and synthesized, and Let-7c degraded the H19 binding site of wild-type effectively (e), and no significant results of Let-7c was detected in groups of H19 of mutant binding region (f). Results were acquired and calculated from three independent experiments.
