Figure 4.
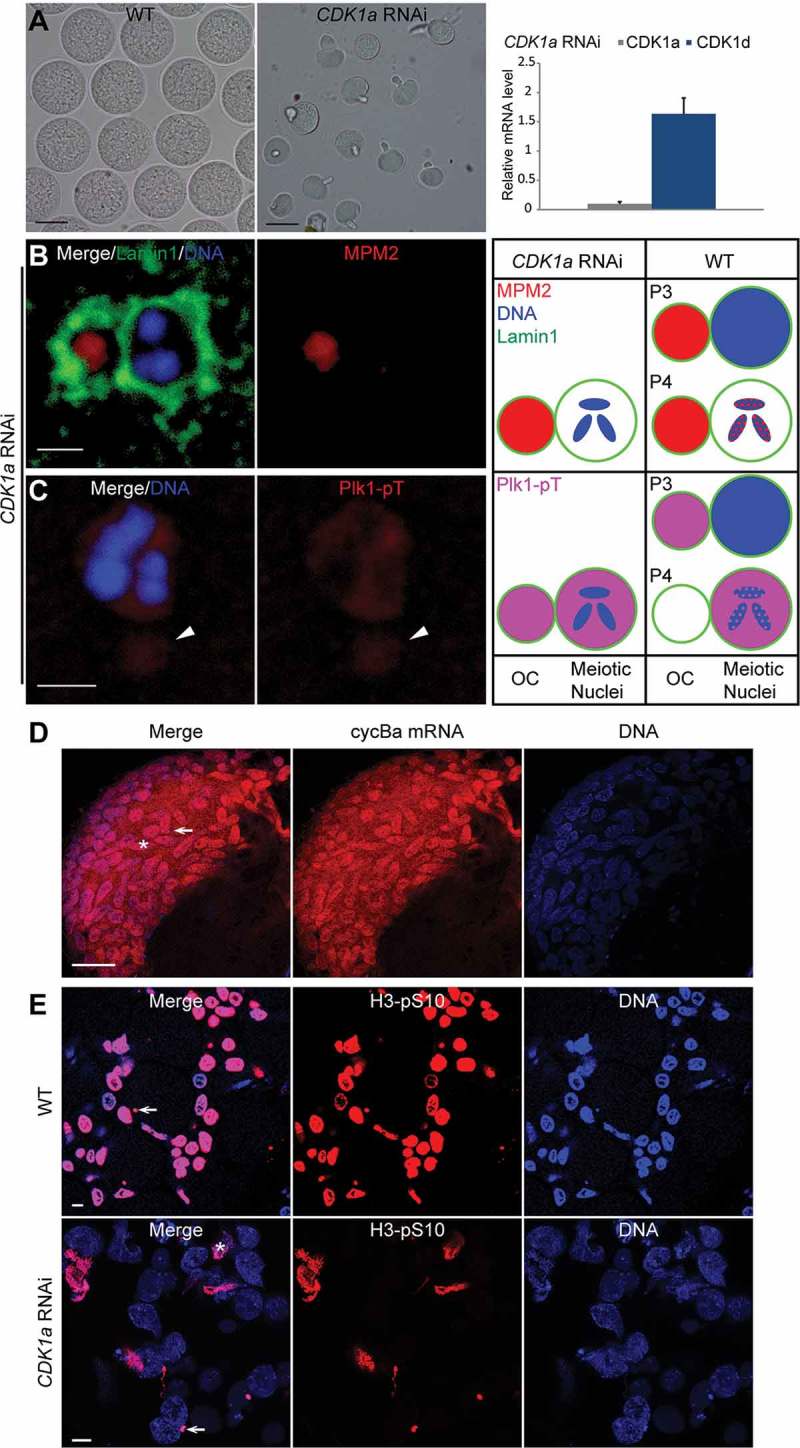
Meiotic defects resulting from CDK1a RNAi. (A) CDK1a RNAi oocytes (mid panel) were smaller than wild-type oocytes (left panel). Scale bars: 50 µm. In the right panel, CDK1a knockdown efficiency was confirmed by RT-qPCR. No significant off-target effects on other CDK1 paralogs were detected. (B) Lamin1 staining showed that CDK1a RNAi oocytes retained OC around meiotic nuclei. MPM2 epitopes were present on OC but absent in meiotic nuclei. Scale bar: 2 µm. (C) Plk1 was absent on chromosomes, but present in nucleoplasm and on OC (arrowhead). Scale bar: 2 µm. Schemas on the right compare the localizations of MPM2 epitopes (red) and Plk1 (pink) in meiotic nuclei and on OC between CDK1a RNAi oocytes and wild type in P3 and P4. (D) in situ hybridization showed that cyclin Ba mRNA (red) was retained in nurse nuclei of CDK1a RNAi ovaries in late P5 prior to spawning. Arrow indicates a meiotic nucleus, aster indicates a nurse nucleus. Scale bar: 50 µm. (E) In WT, all nurse nuclei underwent apoptosis and became H3-pS10 positive just prior to spawning. In CDK1a RNAi ovaries, only a small proportion of nurse nuclei underwent apoptosis and became H3-pS10 positive just before spawning. Arrow indicates a meiotic nucleus, aster indicates a nurse nucleus. Scale bars: 10 µm.
