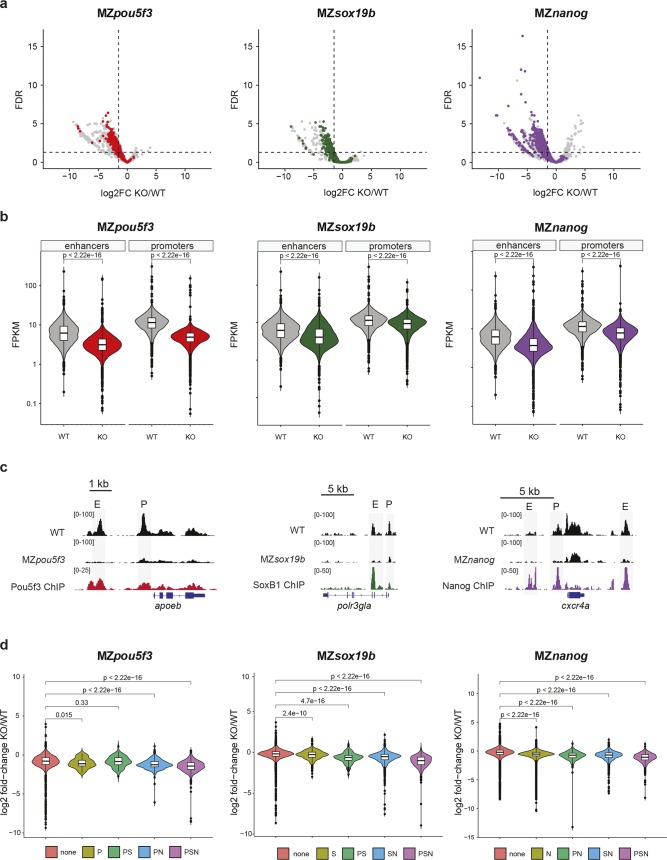
Fig 4. Pou5f3, Sox19b and Nanog regulate chromatin accessibility at gene regulatory elements.
a) Volcano plots showing the log2 fold change in accessibility in MZpou5f3, MZsox19b and MZnanog mutants compared to wild-type embryos at oblong stage. Sites bound by Pou5f1, SoxB1, and Nanog are indicated in red, green and purple respectively. Non-bound sites are indicated in grey. b) Violin plots show the accessibility value (FPKM) at promoters and putative enhancers in wild-type embryos compared to the respective TF mutants. Significance of differences was tested using paired t-tests. c) Genome browser snapshots show accessibility tracks in MZpou5f3, MZsox19b and MZnanog mutants and wild-type embryos at oblong stage, for target genes of the respective TFs [15,25]. ChIP-seq tracks for the respective TFs at blastula stage are from data in [23,24]. d) Violin plots show the log2 fold change in mutants over wild-type at sites bound by different combinations of Pou5f3, SoxB1 and Nanog. p-values are shown for differences between binding sites as assessed by one-sided Wilcoxon tests.