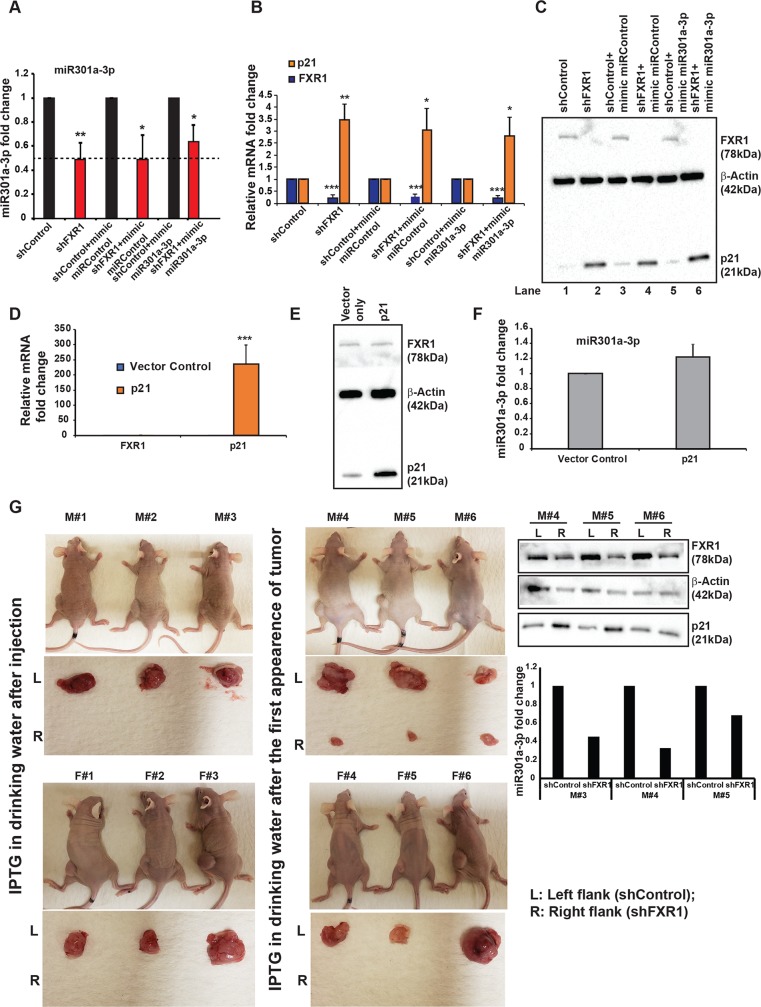
Fig 6. FXR1 and miR301a-3p cooperatively target and repress p21 expression.
(A) qRT-PCR analyses of miR301a-3p in UMSCC74B cells treated with miRNA mimic and scrambled control in the presence and absence of FXR1. RNU6 serves as an endogenous control. (B) qRT-PCR analyses of FXR1 and p21 in UMSCC74B cells treated with miRNA mimic and a scrambled control in the presence and absence of FXR1. ACTIN and RPS18 serve as an endogenous control. (C) Western blot analyses of FXR1 and p21 from UMSCC74B treated with miRNA mimic and a scrambled control in the presence and absence of FXR1. β-Actin serves as a loading control. (D) qRT-PCR analyses of FXR1 and p21 in UMSCC74B cells transfected with p21 overexpression plasmid and vector control. ACTIN and RPS18 serve as an endogenous control. (E) Western blot analyses of FXR1 and p21 from UMSCC74B cells transfected with p21 overexpression plasmid and vector control. β-Actin serves as a loading control. (F) qRT-PCR analyses of miR301a-3p in UMSCC74B cells transfected with p21 overexpression plasmid and vector control. RNU6 serves as an endogenous control. (G) Tumor image from 12 mice injected with UMSCC74B cells expressing IPTG inducible control and FXR1 shRNA clones and treated with 10mM IPTG/5% glucose in the drinking water. Tumors obtained from Male# 4–6 were used for western blot analyses for FXR1 and p21 where β-Actin serves as a loading control and qRT-PCR for miR301a-3p, RNU6 serves as an endogenous control. Data here represent the mean of n = 3 experiments. Statistical significance (p-value): *<0.05; **<0.005; ***<0.0005.