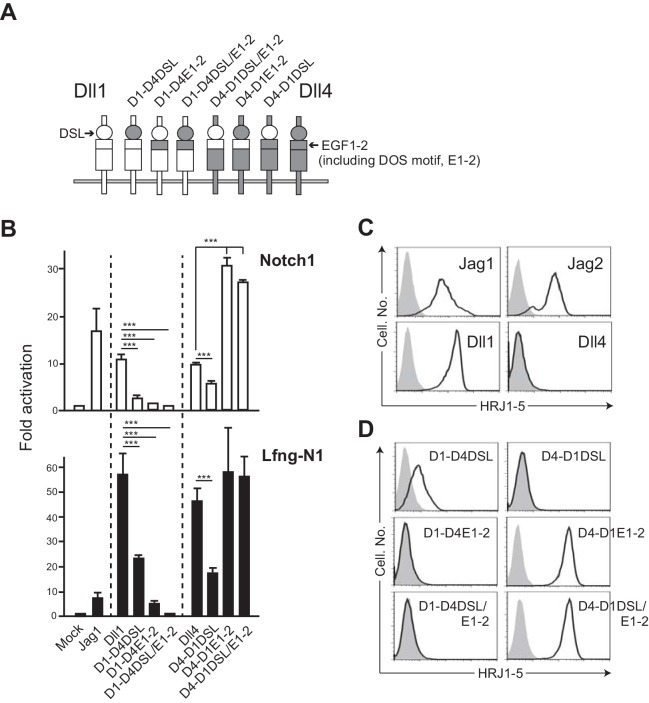
Figure 3. The swapping chimeras of DSL domain and/or the 1st/2nd EGF-like repeats between Dll1 and Dll4.
(A) Schematic structure of the Dll variants. Dll1 and Dll4 were intact and depicted by open (Dll1) or filled (Dll4) columns. The DSL domain and the 1st/2nd EGF-like repeats (E1-2) were represented by circle and top region of square, respectively. D1-D4DSL, D1-D4E1-2, and D1-DSL/E1-2 were Dll1-based chimeras with Dll4-derived DSL domain and/or E1-2. Similarly, Dll4-based chimeras were generated with Dll1-derived domains (D4-D1DSL, D4-D1E1-2, and D4-D1DSL/E1-2). Expression of NotchLs were monitored by GFP expression (Figure 3—figure supplement 2). (B) The swapping chimeras of DSL domain and/or the 1st/2nd EGF-like repeats transduce Notch signaling. Stable transfectants expressing murine Notch1 and control vector (Notch1, open column) or Notch1 and Lfng (Lfng-N1, filled column) were transiently transfected with a TP1-luciferase reporter plasmid, pGa981-6, and a pRL-TK plasmid for internal control. Cells were harvested at 24 hr after transfection, and co-cultured for an additional 40 hr with the transfectants expressing the DSL/E1-2 swapping chimeras. The relative induction of luciferase activity in each sample (mean ± SD, n = 3; ***, p<0.001; unpaired Student’s t-test) was calculated and described as fold activation against the control (value from the culture with mock transfectant not expressing Notch ligand). Data represents three independent experiments. (C) Monoclonal antibody originally established by us, HRJ1-5, broadly reacted with murine Jag1, Jag2, and Dll1, but not with Dll4. The transfectants of BM-derived mesenchymal cell line, originally not expressing any Notch ligands, established in our lab, expressing murine Jag1, Jag2, Dll1, or Dll4, were stained with HRJ1-5, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Open histograms indicate HRJ1-5 staining and filled histograms indicate staining with control hamster IgG. (D) Reactivity of HRJ1-5 with Dll chimeras. Each transfectant shown in the panel was stained with HRJ1-5 and analyzed as in C.