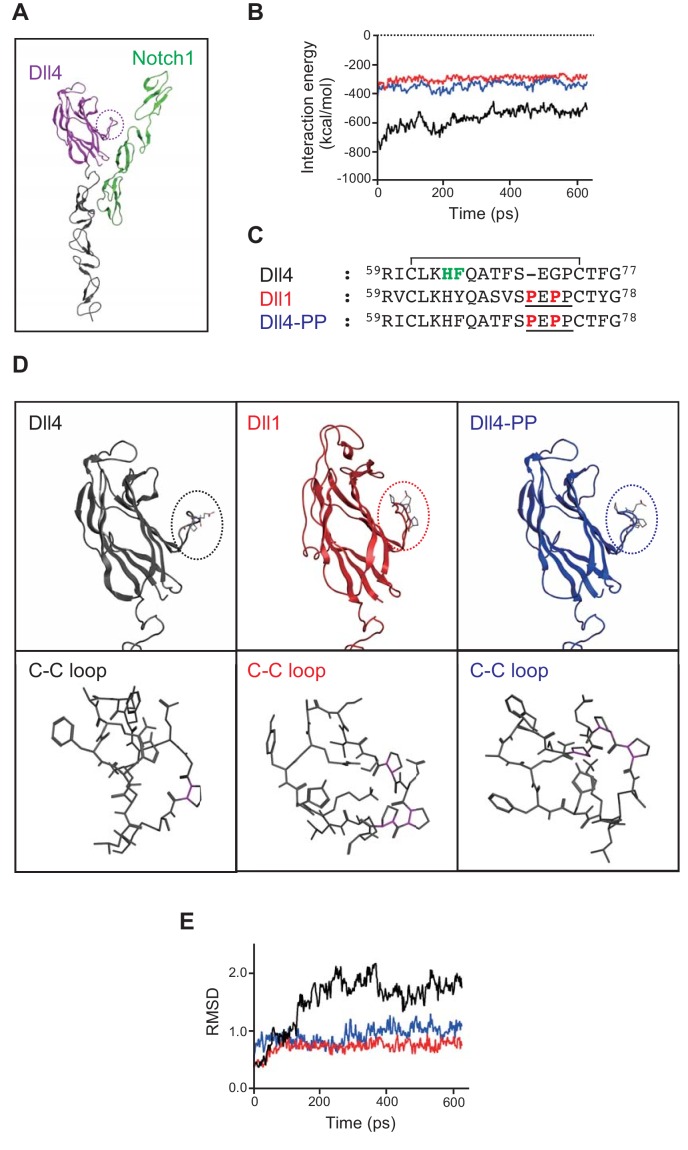
Figure 5. In silico analysis of Dll/Notch1 complexes.
(A) Structure of Dll4 (MNNL, purple; DSL and EGF1-2, black) bound to Notch1 (EGF11-13, green) is shown in ribbon representation. The dotted circle indicates the loop structure with disulfide bond (C-C loop) in MNNL domain. (B) Molecular dynamic simulation of 600 ps for the interaction energy of Dll4/Notch1 (black), D4-D1MNNL/Nothc1 (red), and Dll4-based mutant with two proline residues (characteristic of Dll1) (Dll4-PP/Notch1, blue). (C) Amino acid (AA) sequence comparison of the C-C loop in MNNL domain between Dll4, Dll1, and Dll4-PP. Numbers on the AA sequences represent the position from the N-terminus. D4-PP is the Dll4-based mutant with the inserted (71st position) and substituted (73rd position) mutations of proline residue (bold red; characteristic of Dll1, underline). The AAs in the C-C loop contributing to the direct binding with Notch receptor are labeled (bold green) described as previously. Line over the sequence represents the disulfide bridge between cysteine residues (61st to 74th). (D) Structure of MNNL domain of Dll4 (black), Dll1 (red), and Dll4-PP (blue) in ribbon representation (upper panels) with enlarged wireframe model of the C-C loop (lower panels). Magenta, C-N bond in proline. (E) Molecular dynamic simulation of 600 ps for the RMSD of the C-C loop in the MNNL domain of Dll4 (black), Dll1 (red), and Dll4-PP (blue).
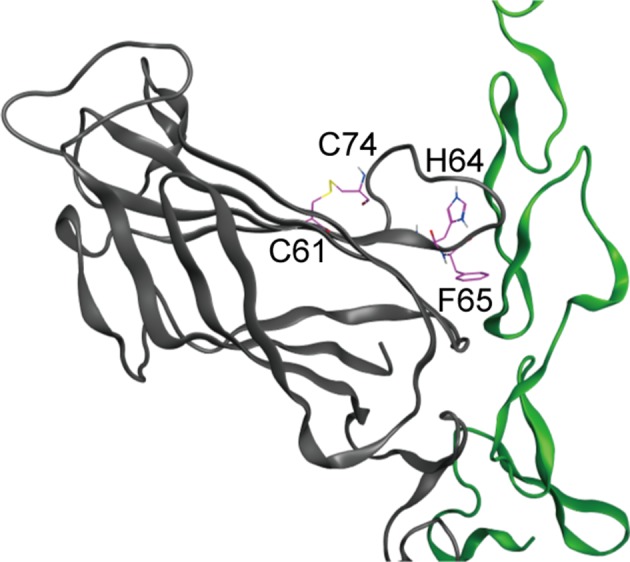
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. The loop structure with disulfide bond between 61Cys (C61) and 72Cys (C72) includes the key residues, 64His (H64) and 65Phe (F65), filled circle in Figure 5C, that comprise the binding surface of MNNL domain of Dll4 which interacts with Notch1.