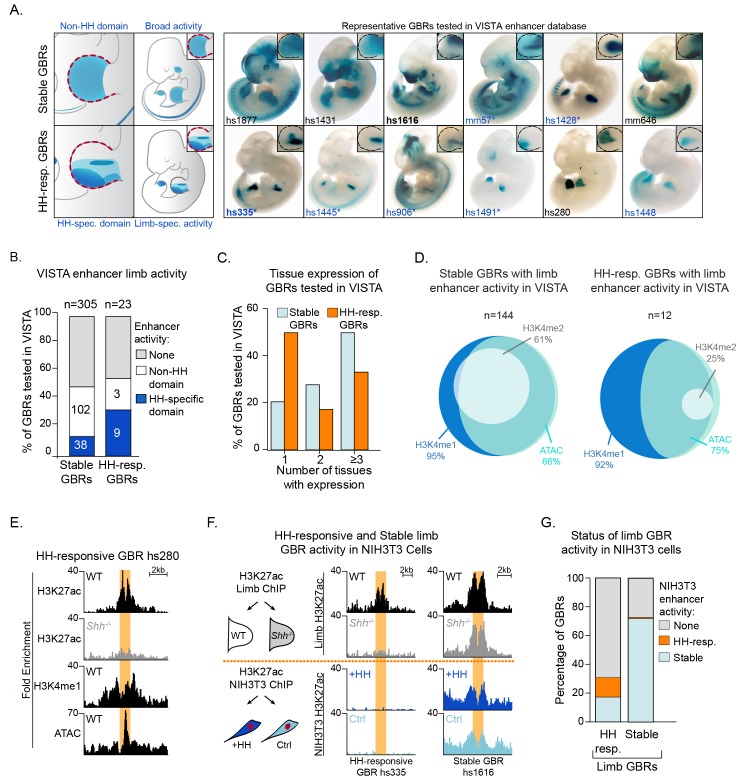
Figure 6. Hedgehog-responsive GBRs have tissue-specific enhancer activity within HH-specific domains.
(A) Enhancers with annotated limb activity in VISTA corresponding to representative HH-responsive GBRs (bottom) and Stable GBRs (top) with limbs magnified and outlined in insets. Limb buds containing HH-specific domains of enhancer activity are indicated by an asterisk. (B) Chart indicating total number of VISTA enhancers tested for HH-responsive and Stable GBRs, the numbers of enhancers for each category and their limb enhancer activity. (C) Chart delineating the percentage of HH-responsive and Stable limb enhancers that drive expression in one or more tissues. (D) Venn Diagram of enhancer marks H3K27ac, H3K4me1, H3K4me2 and ATAC, in Stable and HH-responsive GBRs tested in VISTA that drive expression in the limb. GBRs, are by definition are marked by H3K27ac. (E) Enrichment of enhancer markers at a representative HH-responsive GBR tested in VISTA (hs280, Figure 6A). (F) Schematic of NIH3T3 H3K27ac ChIP treated with and without the HH agonist purmorphamine (+HH) and the activity of representative HH-responsive and Stable limb GBRs in response to HH activation in limb and NIH3T3 cells (n = 2). (G) Graph indicating how the acetylation status of HH-responsive and Stable limb GBRs responds to HH signaling in HH-responsive NIH3T3 cells. See Figure 6—source data 1; Figure 6—source data 2.