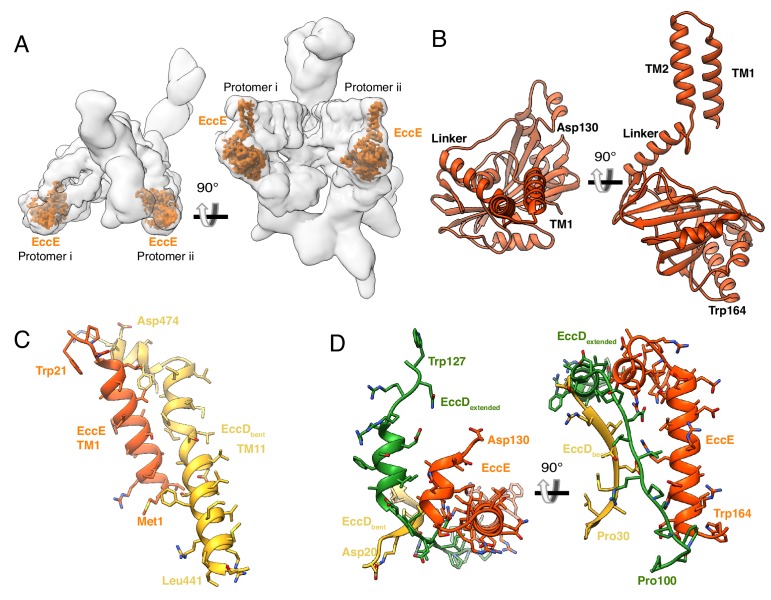
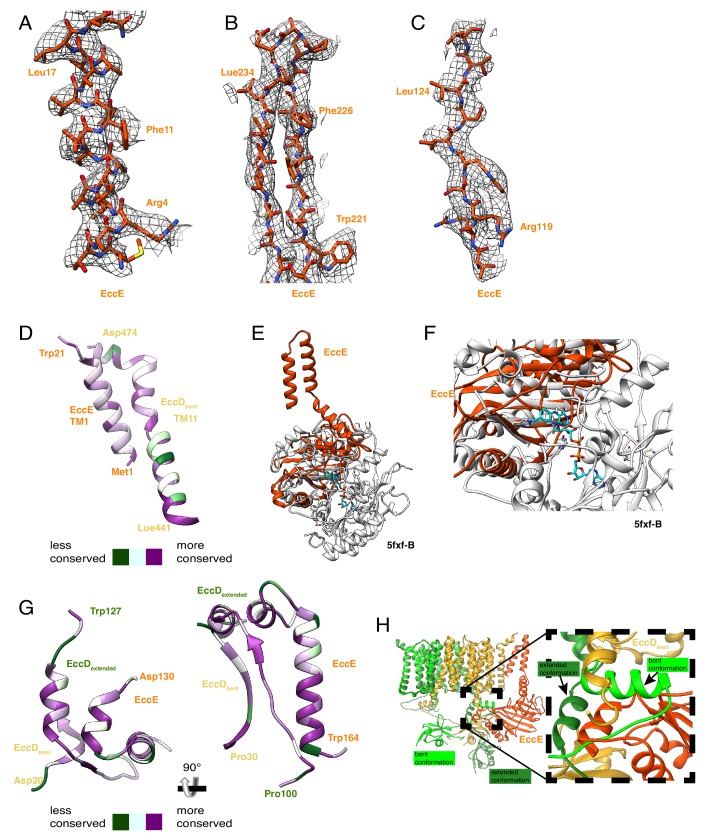
Figure 3. The structure and protein-protein interactions of EccE3.
(A) The placement of EccE3 in the overall ESX-3 dimer. (B) Atomic model of EccE3 (C) Transmembrane helix 1 of EccE3 interacts with transmembrane helix 11 of EccD3-bent (D) Two soluble helices of EccE3 interact with EccD3-extended and EccD3-bent.