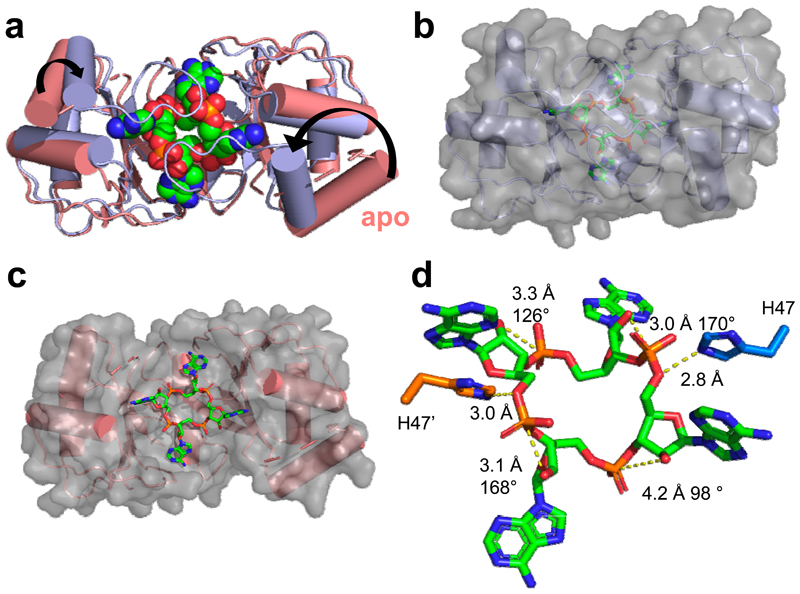
Figure 3. Structure of AcrIII-1 bound to cA4.
(a) Superimposition of the apo SIRV1 gp29 structure (salmon) and in complex with cA4 (blue), highlighting the movement of the loop and α-helix upon cA4 binding. cA4 is shown coloured by element. (b) Surface representation of the structure of SIRV1 gp29 (blue) in complex with cA4, emphasising the complete burial of the ligand. (c) Surface representation of the apo structure of SIRV1 gp29 (salmon) with cA4 in the position observed in the complex structure, indicating that the binding site is pre-formed. (d) Structure of cA4 bound to SIRV1 gp29. The two active site histidine residues (modelled based on the position of the alanine side chain in the H47A variant crystallised with cA4; coloured to represent residues from different monomers) are in suitable positions to act as the general acid, protonating the oxyanion leaving group. The corresponding ribose sugars have 2’-hydroxyl groups suitably positioned for in-line nucleophilic attack on the phosphodiester bond.