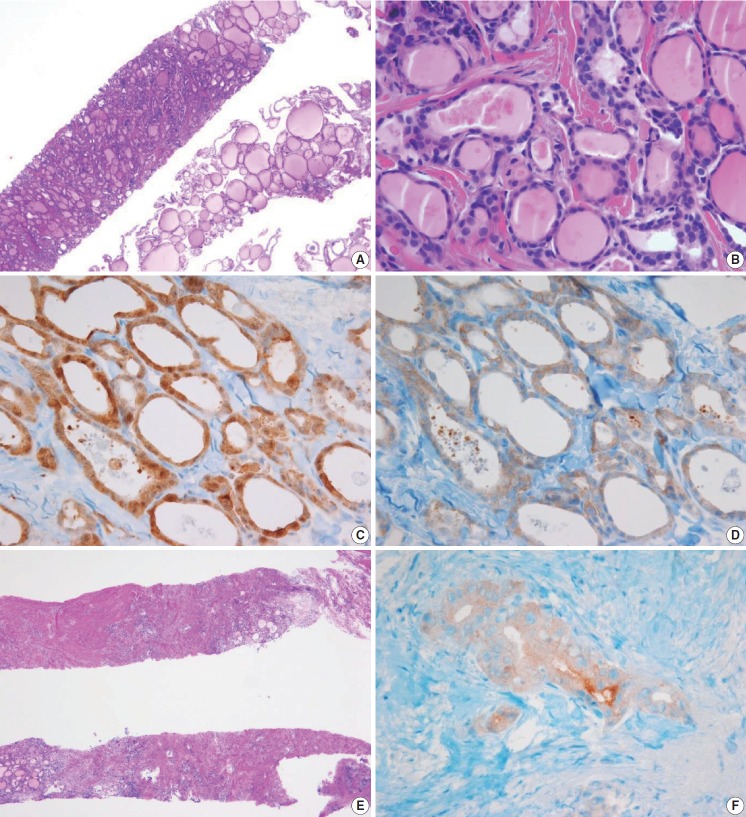
Fig. 9.
(A) The specimen shows a follicular proliferative lesion with an ill-defined border showing a different morphology compared with adjacent normal thyroid tissue. (B) The high-power view in Fig. 9A reveals atypical follicular cells with nuclear atypia and fibrous bands. These morphological features can be interpreted as suspicious for papillary carcinoma (category V). In this case, immunohistochemical stains for galectin-3 (C) and BRAF VE1 (D, F) facilitate the diagnosis of papillary carcinoma. (E) A paucicellular, hyalinized follicular lesion exhibits morphological features pathognomonic for papillary carcinoma. The diagnosis of the lesion can be established as papillary carcinoma when atypical follicular cells in the specimen are positive for BRAF VE1 immunostaining (F).