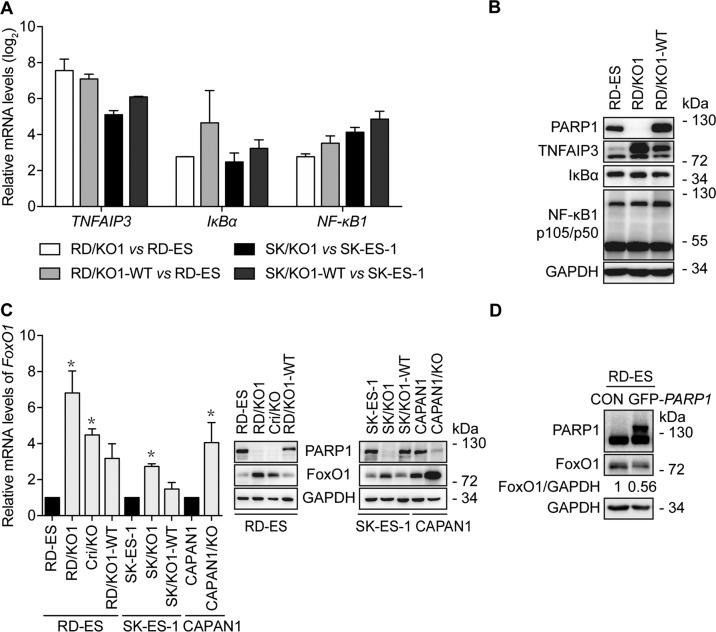
Fig. 2. PARP1 loss increases FoxO1 expression.
a Confirmation of some results from RNA-seq by RT-qPCR in different cells. Log2 mRNA levels of TNFAIP3, IκBα, and NF-κB1 in PARP1-KO or complemented cells were normalized to that in corresponding parental cells. Error bars represent the SD. b Confirmation of some results from RNA-seq by western blotting in indicated cells. c Loss of PARP1 increased mRNA and protein levels of FoxO1, which was prevented, at least partially, by PARP1 complementation. The mRNA levels of FoxO1 were detected by RT-qPCR and normalized to that in the corresponding parental cells; Error bars represent the SD. *, p < 0.05. Protein levels of FoxO1 were detected by western blotting. d After RD-ES cells were transfected with GFP-PARP1 cDNA for 72 h, protein levels of FoxO1 were determined by western blotting. The relative FoxO1 levels were presented as the ratio of (FoxO1/GAPDH)GFP-PARP1/(FoxO1/GAPDH)CON when the value of (FoxO1/GAPDH)CON was normalized as 1.