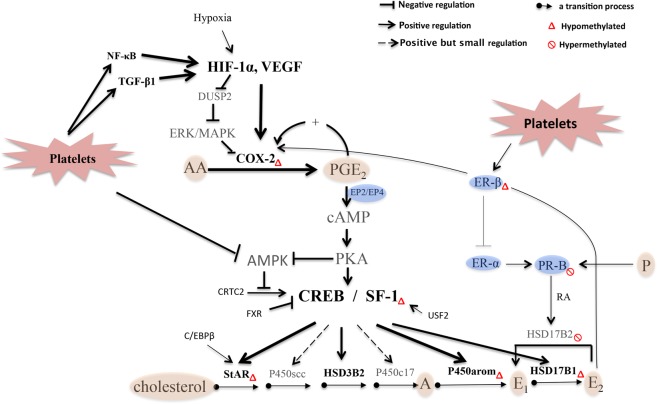
Figure 8.
A schematic diagram that depicts platelet-induced estrogen biosynthesis in endometriosis. Activated platelets induce the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway and TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway in endometriotic lesions21. The two signaling pathways regulate several genes coding for hypoxia and inflammatory molecules, such as HIF-1α, COX-2 and VEGF99–101, which are upregulated after platelets treatment in HESCs. Activated platelets induce hypoxia in endometriotic lesions as shown by elevated expression of HIF-1α and VEGF. Increased HIF-1α accumulation results in DUSP2 down-regulation, which results in prolonged activation of ERK and p38 MAPK and increased COX-2 expression in endometriotic stromal cells49, as well as increased ERβ expression66 which can also be induced by activated platelets. The COX-2 overexpression leads to increased production of PGE2 in endometriosis, further favor E2 synthesis in HESCs. High levels of local E2 (through ERβ) and PGE2 in turn may further amplify COX-2 expression83, which results in overexpression of steroidogenic genes, and continuous local production of E2 and PGE2 in endometriotic tissue. PGE2 increases intracellular cAMP levels via the receptors EP2 or EP4102. Elevated cAMP upregulates SF-1 and enhances its binding to the promoter of steroidogenic genes15, as well as PKA activation, resulting in the phosphorylation of CREB which facilitates its binding to a cAMP-response element (CRE) on the promoter region of the StAR, aromatase or some other steroidogenic genes45,103, and acts as an initiator to unfold the DNA-histone binding and then provides space for C/EBP binding to the promoter of these steroidogenic genes. PGE2-induced StAR promoter activity appears to be regulated by CREB and C/EBPβ in a cooperative manner in endometriotic stromal cells16. PGE2 negatively regulates AMPK via the PKA signaling pathway104, and CREB and related proteins are also the direct downstream targets for AMPK105. AMPK is crucial for the activation of CREB via phosphorylation and there is a negative regulatory role of AMPK in the expression of CREB106. CRTC2 is translocated into the nucleus, where it forms a transcription complex with CREB107. AMPK can directly phosphorylate CRTC family members. In the absence of AMPK activity, CRTC2 is dephosphorylated and translocated to the nucleus and associates with CREB, and then increases target gene expression108. Activated platelets also inhibit AMPK activation via downregulation the phosphorylation level of AMPK in HESCs (Qi et al., unpublished data), which can further activate the CREB binding to steroidogenic genes in HESCs. In addition, it reported that USF2 binds to the SF-1 promoter, and stimulates the expression of SF-1 and its target genes109, and recent research has shown that FXR competes with CREB in binding the promoter region of CYP19A1, which results in the downregulation of aromatase expression110. Progesterone induces the expression of epithelial HSD17B2 by activating stromal PR-B, which can mediate the formation of retinoid acid to bind to the promoter and thus activate HSD17B2. In endometriotic tissues, the decreased PR-B expression in stromal cells disrupts the paracrine action of progesterone. ERβ suppresses ERα and PR-B, leading to progesterone resistance and deficient inactivation of E2 in endometriotic lesions. Abbreviations used: AA: arachidonic acid, PGE2: prostaglandin E2, RA: retinoic acid, COX-2: cyclooxygenase-2, A: androstenedione, E1: estrone, E2: estradiol, P: progesterone, SF-1: steroidogenic factor-1, CREB: cAMP-response element-binding protein, StAR: steroidogenic acute regulatory, P450scc: cytochrome P450 side-chain cleavage, HSD3B2: 3-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2, P450c17: cytochrome P450 17α-hydroxylase/17, 20-lyase, HSD17B1: 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1, HSD17B 2: 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2. ER-α: Estrogen receptor-α; ER-β: Estrogen receptor-β. PR-B: progesterone receptor B, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase, AMPK: AMP-Activated Protein Kinase, CRTC2: CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2, C/EBPβ: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β, USF2: Upstream stimulatory factor 2, FXR: Farnesoid X Receptor.