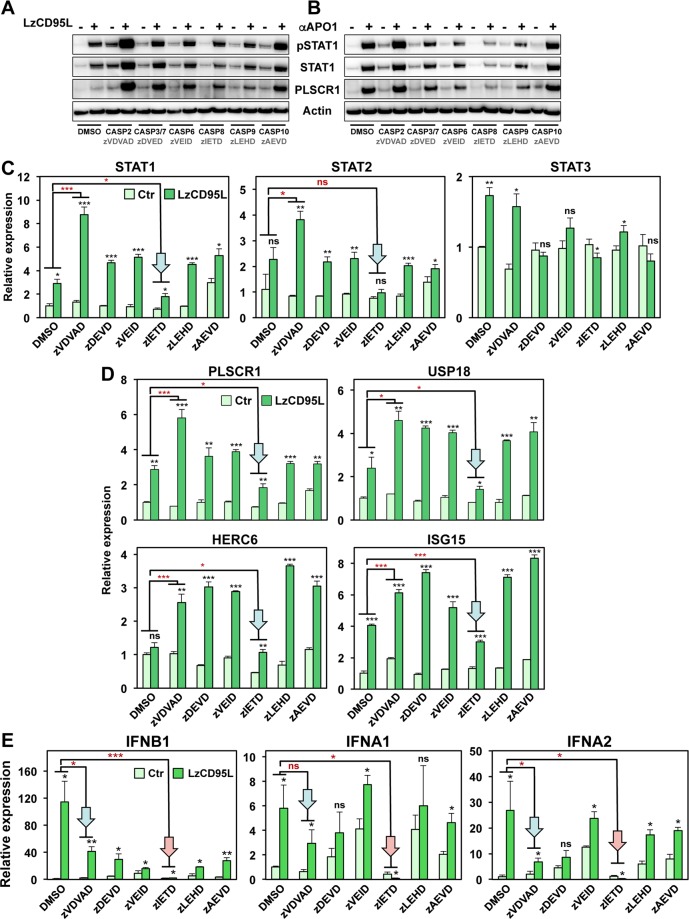
Figure 2.
Effect of different caspase inhibitors on STAT1 activation and STAT1 target gene expression in CD95 stimulated cells. (A,B) Western blot analysis of MCF-7 cells treated with either DMSO solvent control, 20 μM of an inhibitor of caspase-2 (zVDVAD), caspase-3/7 (zDEVD), caspase-6 (zVEID), caspase-8 (zIETD), caspase-9 (zLEHD), or caspase-10 (zAEVD) upon LzCD95L (A) or anti-APO-1 (B) treatment for 4 days. All uncropped immunoblot images are included in Fig. S9. (C) Real-time PCR quantification of mRNAs in MCF-7 cells treated as shown in A upon exposure to LzCD95L for 4 day. (D) Real-time PCR quantification of mRNAs in MCF-7 cells treated as in A. Error bars represent the SD of three biological replicates. (E) Real-time PCR quantification of mRNAs in MCF-7 cells treated as in A. Student’s t-test was performed compared to matching control. A linear model for continuous gene expression levels, using binary predictors for LzCD95L and zVDVAD or zIETD and their interaction term, was used to evaluate whether the effect of LzCD95L on gene expression varied depending on the presence of zVDVAD or zIETD (red asterisks). p-value *<0.05, **<0.001; ***<0.0001; ns, not significant.