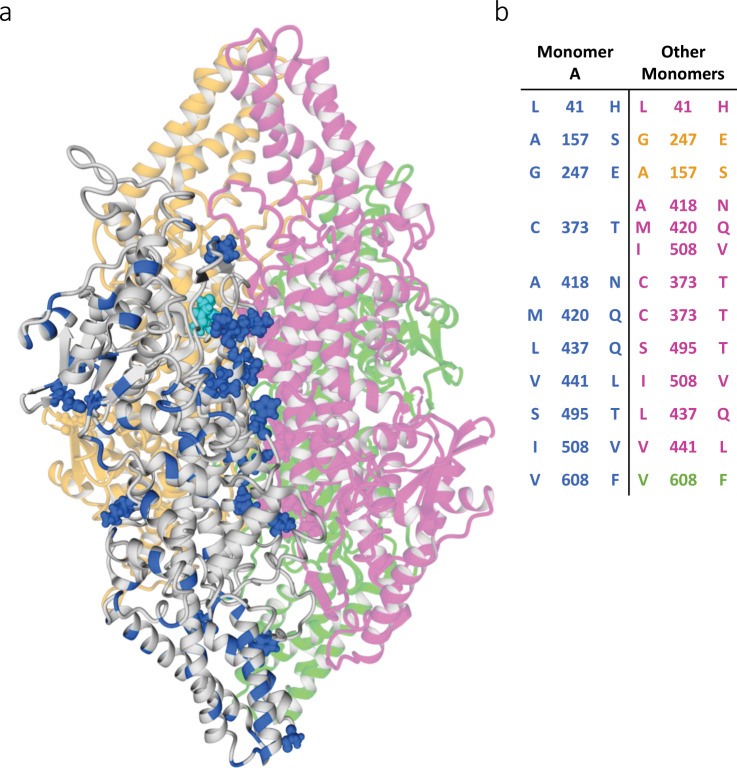
Figure 3.
Ancestral PAL/TALs form tetramers despite non-conserved interfaces between monomers. (a) Homology model of MEGA_A1 showing the distribution of ancestral mutations. Monomers are coloured in grey (monomer A), magenta (monomer B), yellow (monomer C) and green (monomer D). All ancestral mutations are coloured in blue in monomer A, and surface mutations within 4 Å of another monomer are shown as balls. Catalytically active group MIO is shown in cyan for monomer A for reference of the active site location. The model was built in YASARA using the crystal structure of PAL/TAL from Rhodotorula turoloides (PDB, 1Y2M7) as a template. (b) Possibly coupled ancestral mutations in the oligomerization interfaces. The mutations for monomer A are listed in blue and the corresponding mutations in proximity are coloured according to monomer. Mutations are noted with RgPAL residues on the left and the corresponding residue in MEGA_A1 on the right.