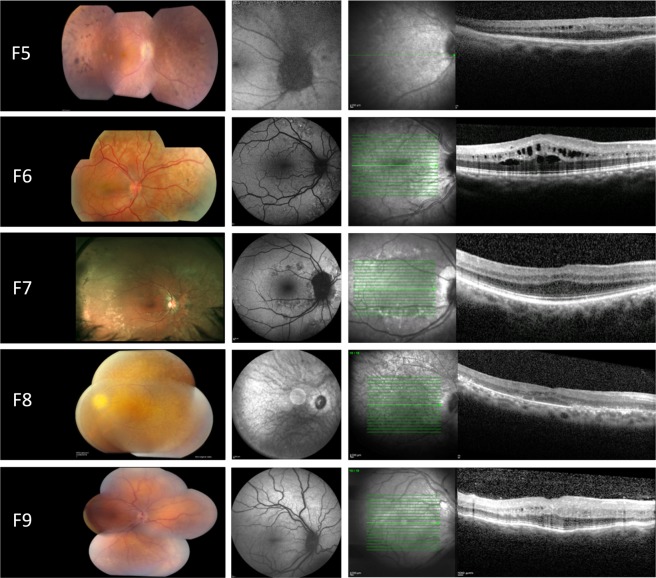
Figure 2.
Retinal imaging from the right eye of patients with NNO or MCOP due to mutations in MFRP. Left panel: color fundus. Middle panel: fundus autofluorescence imaging (FAF). Right panel: optical coherence tomography (OCT). F5: color fundoscopy showing crowded optic disc, mid-peripheral intraretinal hyperpigmentation with corresponding hypo-autofluorescence on FAF, foveal hypoplasia and intraretinal cystic cavities on OCT. F6: mid-peripheral hypopigmentary retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) changes with corresponding hyper- and hypo-autofluorescence on fundus autofluorescence imaging (FAF), cystic macular cavities on optical coherence tomography (OCT). F7: posterior pole and mid-peripheral hyper- and hypo-pigmentary RPE change with corresponding hyper- and hypo-autofluorescence on FAF, thickened OCT with foveal hypoplasia. F8: color fundoscopy with crowded optic disc, slight peripheral intraretinal hyperpigmentation and large posterior pole white dots corresponding with hyper- and hypo-autofluorescence on FAF imaging, foveal hypoplasia and cystic macular cavities on OCT. F9: color fundoscopy showing crowded optic disc and normal autofluorescence on FAF imaging, thickened OCT with foveal hypoplasia and occasional intraretinal cyst.