Figure 1.
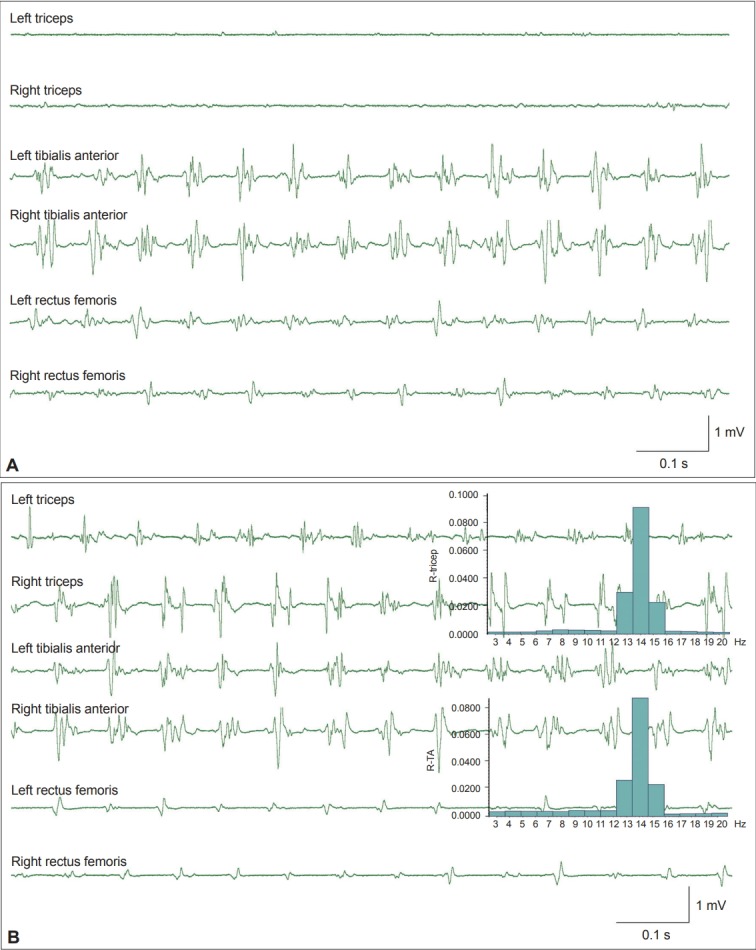
Example of orthostatic tremor. A: Surface electromyography (sEMG) signals recorded from a patient with orthostatic tremor. EMG bursts in the bilateral rectus femoris and tibialis anterior muscles reveal regular firing at a frequency of 14 Hz. B: The patient leaned forward and partially supported his weight with both arms by pressing on a table. Tremors at 14 Hz are now evident in both triceps muscles that are used for support. The inset histograms show the same power spectrum peak at 14 Hz in both the triceps and the tibialis anterior muscles. R-TA: right tibialis anterior muscle.
