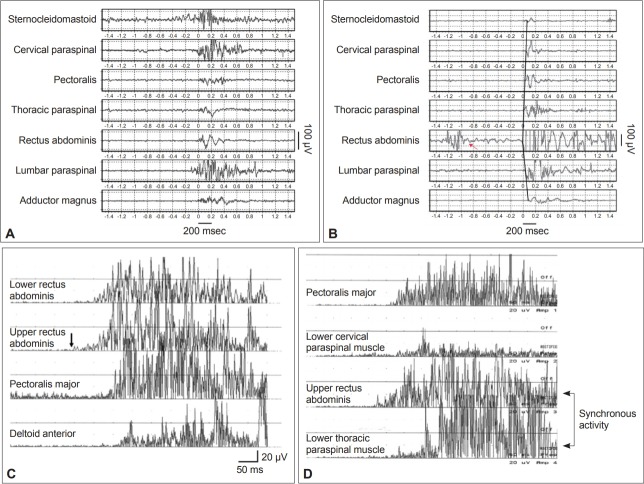
Figure 6.
Functional propriospinal myoclonus (PSM) and PSM mimicked by healthy subjects. Functional PSM can sometimes be differentiated from idiopathic or symptomatic PSM by (A) the absence of a typical rostral and caudal recruitment order, (B) a burst duration longer than 1,000 ms and isolated muscle activity in the rectus abdominis muscle (red arrow). PSM symptoms can be mimicked. Healthy subjects can mimic (C) typical PSM propagation patterns starting from the upper rectus abdominus muscle (black arrow) and (D) synchronous activation of the truncal flexors and extensors. Adapted from Erro et al.[56] and Kang and Sohn[55].