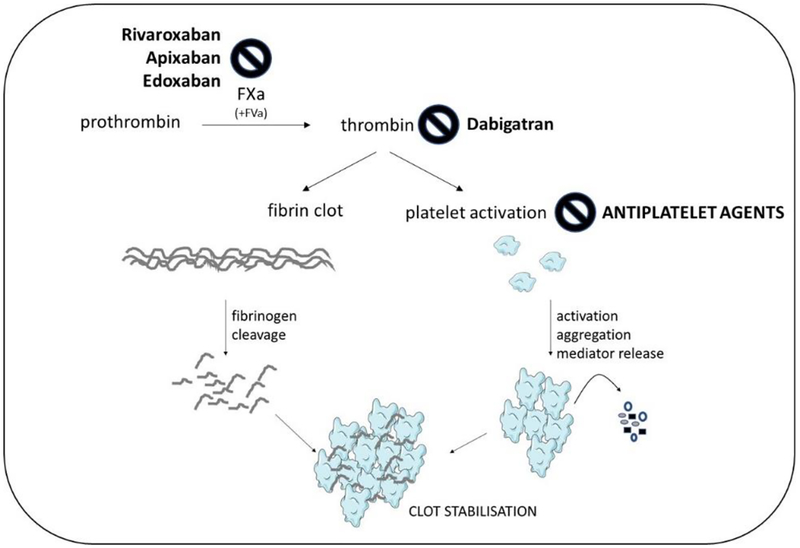
Fig. 1: DOAC inhibition sites.
Coagulant pathways converge in a common step culminating in the FXa-mediated proteolysis of prothrombin to active thrombin. Thrombin potently activates platelets and cleaves fibrinogen to fibrin, leading to clot stabilization. Classic antiplatelets agents prevent secondary platelet activation. The DOAC either inhibit FXa enzymatic activity and hence thrombin activation, or directly inhibit thrombin. The vitamin K-dependent oral anticoagulants like warfarin by contrast suppress block coagulant activity indirectly by preventing synthesis of the precurser factors FII (thrombin), FVII, FIX and FX.