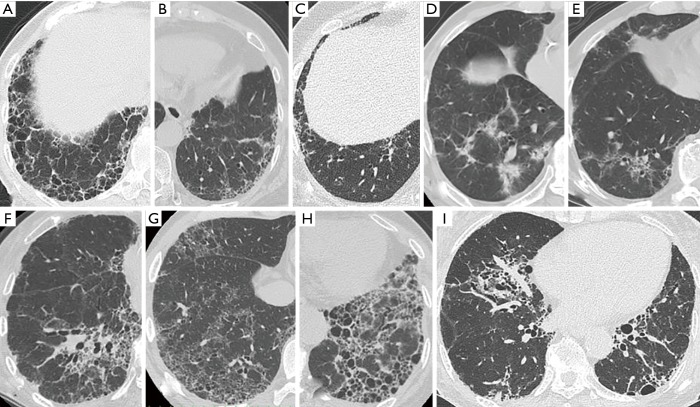
Figure 2.
High-resolution computed tomography images illustrating each pattern in RA-ILD. (A) Definite UIP pattern: subpleural and basal-predominant reticulation with clustered cystic space as honeycombing; (B) probable UIP pattern: subpleural and basal-predominant reticulation with peripheral traction bronchiectasis or bronchiolectasis; (C) early UIP pattern: mild reticulation or GGO without traction bronchiolectasis; (D,E,F) NSIP pattern: predominant basilar GGO with limited to no reticulation and absent honeycombing; (G,H,I) NSIP/UIP pattern: both central or diffuse distribution of reticulation or GGO as the component of NSIP and subpleural reticulations with or without honeycombing as the component of UIP in the lower lung (G: diffuse GGO and peripheral reticulation without honeycombing; (H,I): both central and peripheral distribution of reticulation and traction bronchiectasis with honeycombing). GGO, ground-glass opacity; ILD, interstitial lung disease; NSIP, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; UIP, usual interstitial pneumonia.