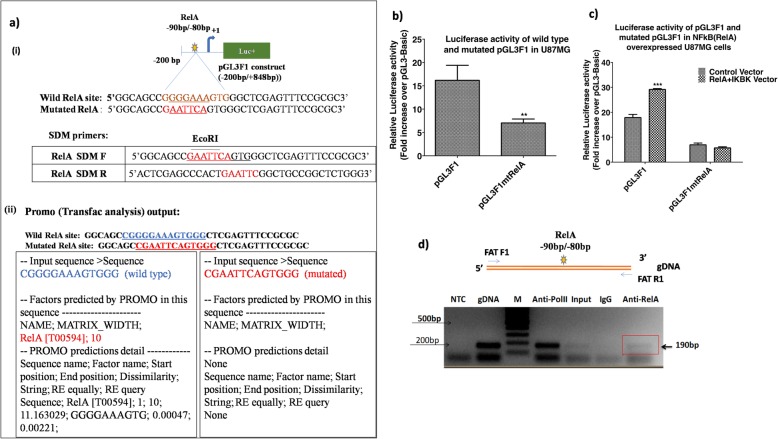
Fig. 7.
Confirmation of functional association of NFкB (RelA) on FAT1 promoter. a i) A representative diagram of pGL3F1 construct (− 200 bp/+ 848 bp) showing -200 bp upstream promoter sequence attached to luciferase reporter gene showing one NFkB (RelA) site (yellow green star) at − 90 bp/− 80 bp. NFkB (RelA) SDM primers are complementary to putative site of NFkB (RelA) site (at -90 bp/− 80 bp) with base (purine and pyrimidine) changes with integrated EcoRI site (5’GAATTC3’). Primer sequence of wild type and mutated NFkB (RelA) site for SDM are given. ii) In-silico validation for wild and mutated NFkB (RelA) site at -90 bp/− 80 bp was done using Promo output. NFkB (RelA) wild type sequence shows NFkB (RelA) binding site while NFkB (RelA) mutated sequence has no NFkB (RelA) binding site. b Effect of site directed mutagenesis of NFкB (RelA) on FAT1 promoter activity. U87MG cells were transfected with FAT1 promoter constructs, pGL3F1 and pGL3F1mtRelA. Promoter luciferase activity was analysed after 48 h. Significant decrease in luciferase activity of pGL3F1mtRelA by 56% was observed as compared to pGL3F1. c Effect of NFкB overexpression on promoter activity of wild type construct (pGL3F1) and mutated construct (pGL3F1mtRelA) in glioma cells. U87MG cells were co-transfected with pGL3F1 + IKBK+RelA, pGL3F1mtRelA + IKBK+RelA, pGL3F1 + eBABE, pGL3F1mtRelA + eBABE and control vector (pGL3Basic + eBABE) for 48 h. Promoter activity in pGL3F1 construct, with wild type NFкB (RelA) binding site, was increased in response to NFкB (RelA) overexpression (pGL3F1 + IKBK+RelA cells). However, promoter activity in pGL3F1mtRelA was reduced by 60% as compared to pGL3F1 construct and did not show any increase after NFкB (RelA) overexpression. Fold luciferase activity was analysed using pGL3Basic (negative control). Values are mean ± SE of three independent experiments performed in triplicates. Statistical analysis was performed using paired two-tailed Student’s t-test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). d ChIP assay. A diagrammatic representation of the ChIP product from FAT1 promoter showing NFкB (RelA) binding site at -90/− 80 bp and primers (FATF1 and FATR1) complimentary to FAT1 gene flanking the NFкB (RelA) motif is shown. Input: sonicated and reverse cross-linked whole gDNA templates U87MG, IgG (negative control): immunoprecipitated with anti-mouse IgG, Anti-RelA: immunoprecipitated with anti-RelA antibody, Anti-Pol II (positive control): immunoprecipitated with anti-Pol II antibody, gDNA: positive PCR control, NTC: no template control, M: marker (100 bp ladder). ChIP product (FAT1) of 190 bp size has been indicated