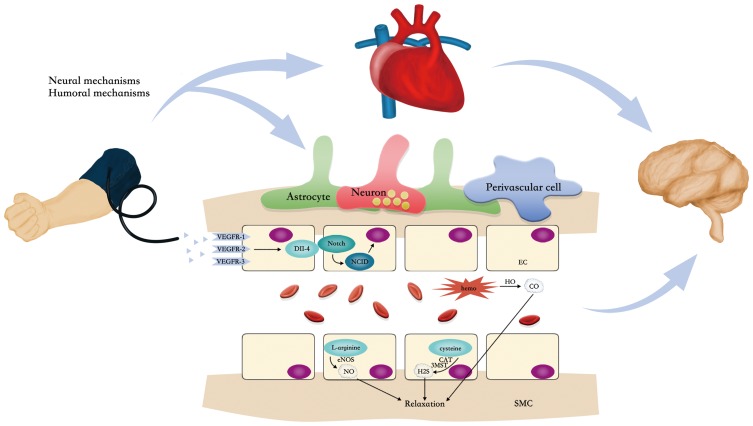
Figure 1.
The simplified schema graph of potential mechanisms through which RIC influences CBF. The hypoxia induced by RIC upregulates the VEGF production, which activates VEGFR. Then, Dll-4 expression is induced and NCID is proteolytically cleaved to liberate an adjacent endothelial cell. NICD enters the nucleus and activates the transcription of Notch-responsive genes. The interaction between VEGF and the Notch signaling pathway plays a crucial role in angiogenesis. RIC can also induce the formation of three main gas molecules: NO, CO, and H2S. They can improve CBF by relaxing smooth muscle cells. RIC can also improve CBF by protecting cardiac function and NVU.
Abbreviations: CAT, cysteine aminotransferase; CBF, cerebral blood flow; CO, carbon monoxide; Dll-4, Delta-like 4; EC, endothelial cell; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; H2S, hydrogen sulfide; HO, heme oxygenase; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; 3MST, 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase; NCID, Notch intracellular domain; NO, nitric oxide; NVU, neurovascular unit; RIC, remote ischemic conditioning; SMC, smooth muscle cell; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.