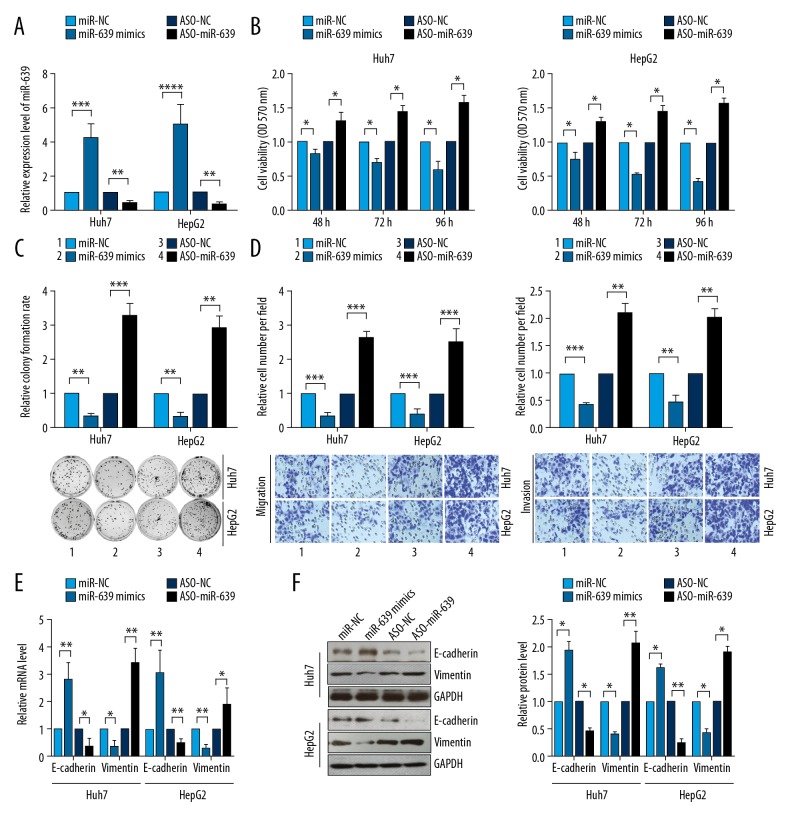
Figure 2.
microRNA-639 (miR-639) inhibited cell proliferation, cell migration, colony formation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines, Huh7 and HepG2. (A) miR-639 expression was detected using quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) in two human HCC cell lines, Huh7 and HepG2. (B) Cell viabilities of HCC cells were analyzed using the MTT assay. (C) Colony formation of HCC cells was assessed by using the colony formation assay. (D) Transwell migration and invasion of human HCC cell lines, Huh7 and HepG2, were studied using transwell assays. (E) Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was performed to evaluate the transcription levels of EMT markers. (F) Western blot was used to detect the expression levels of EMT markers. Studies were performed in triplicate. (* p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001; **** p<0.0001).