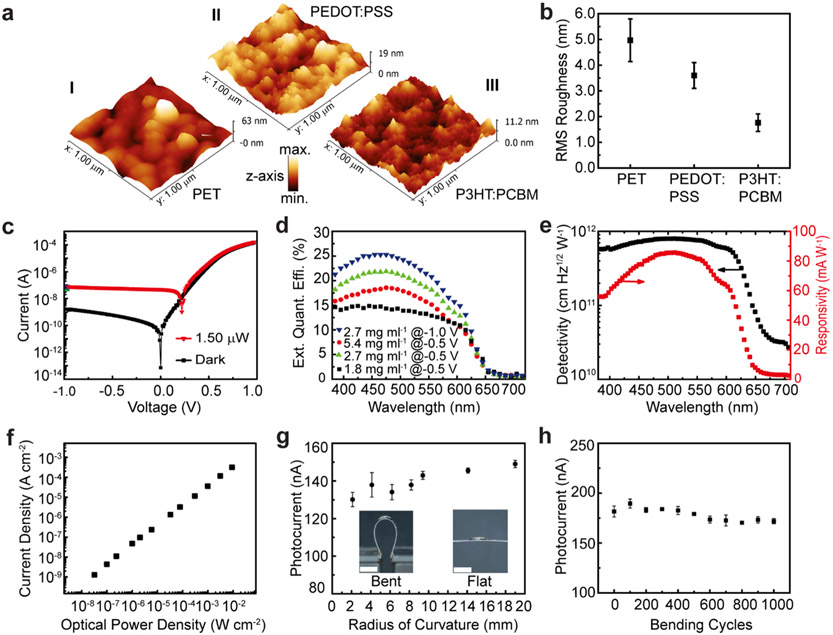
Figure 2.
Characterization of 3D printed photodetectors on PET films. a. Surface morphologies of the 3D printed polymer layers on a PET substrate. I, PET substrate; II, PEDOT:PSS on PET substrate; and III, P3HT:PCBM on PEDOT:PSS/PET substrate. b. RMS roughness of each printed layer (N = 7). c. Current-voltage characteristics of photodetector under dark and 510 nm/1.5 μW illumination. d. EQE of the photodetectors printed with varying P3HT:PCBM ink concentrations. A maximum EQE of 25.3% was achieved with an ink concentration of 2.7 mg ml−1 under −1.0 V bias. e. Specific detectivity and responsivity of the 3D printed photodetector. f. LDR of the 3D printed photodetector under 510 nm illumination. g. Static bending test of the photodetector, excited by a 650 nm laser with a power of 55 μW (N = 5). The insets show the photographs of flat and bent photodetectors. Scale bars are 4 mm. h. Cyclic bending test of the photodetector with a radius of curvature of 6.2 mm, excited by a 650 nm laser with a power of 70 μW (N = 3).