Figure 3.
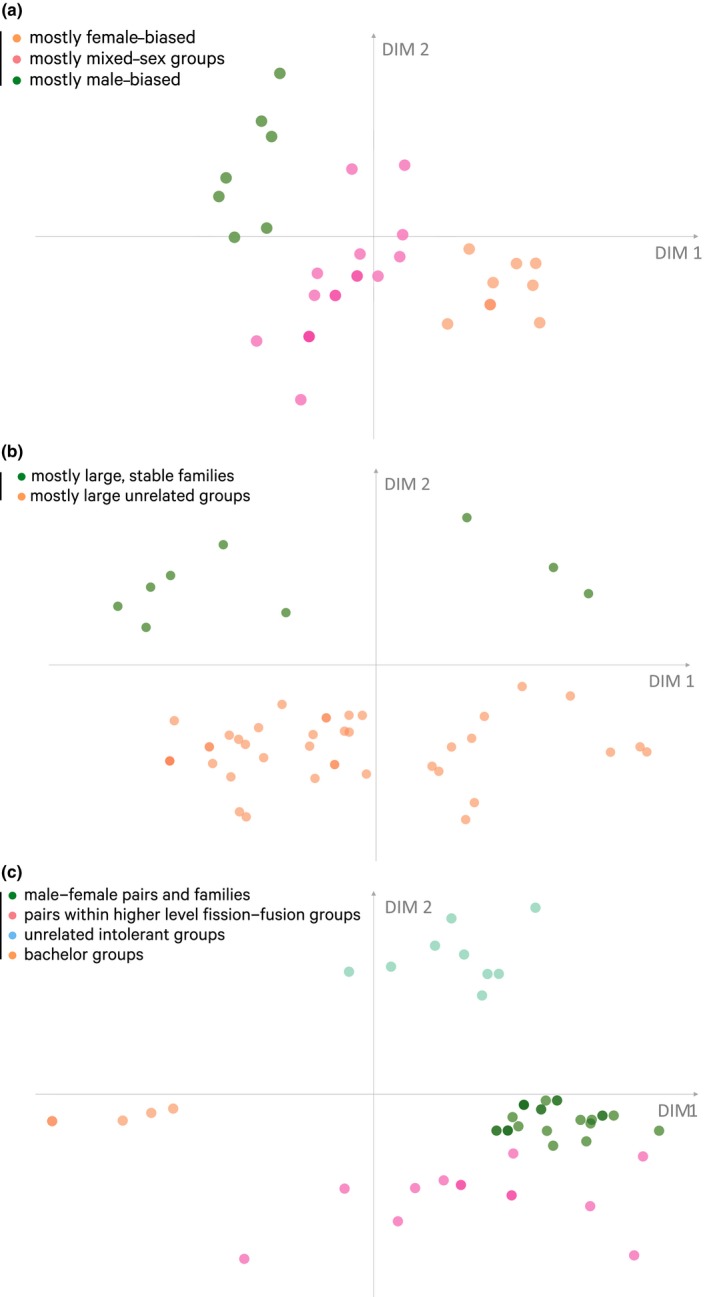
Distribution of society components across cluster landscape within clusters. Social components are positioned and colored using the same technique as Figure 2. (a) Patterns of subclusters from cluster 1: dark green: (seasonally persistent) male–female pairs and families; pink: pairs that form part of a higher level; light blue: unrelated intolerant groups; orange: “bachelor groups”: small unrelated groups of males; dark blue: large unrelated groups with no or short offspring membership. (b) Patterns of subclusters from cluster 2: green subcluster consists of mostly large, stable families with philopatric offspring; orange subcluster consists of mostly large unrelated groups. (c) Patterns of subclusters from cluster 3: the sex ratio of the society components within the orange subcluster is mostly female‐biased, the pink subcluster unbiased, and the green subcluster consists of social components with male‐biased sex ratios. The results from the corresponding genus‐level analyses are given in Figure A4
