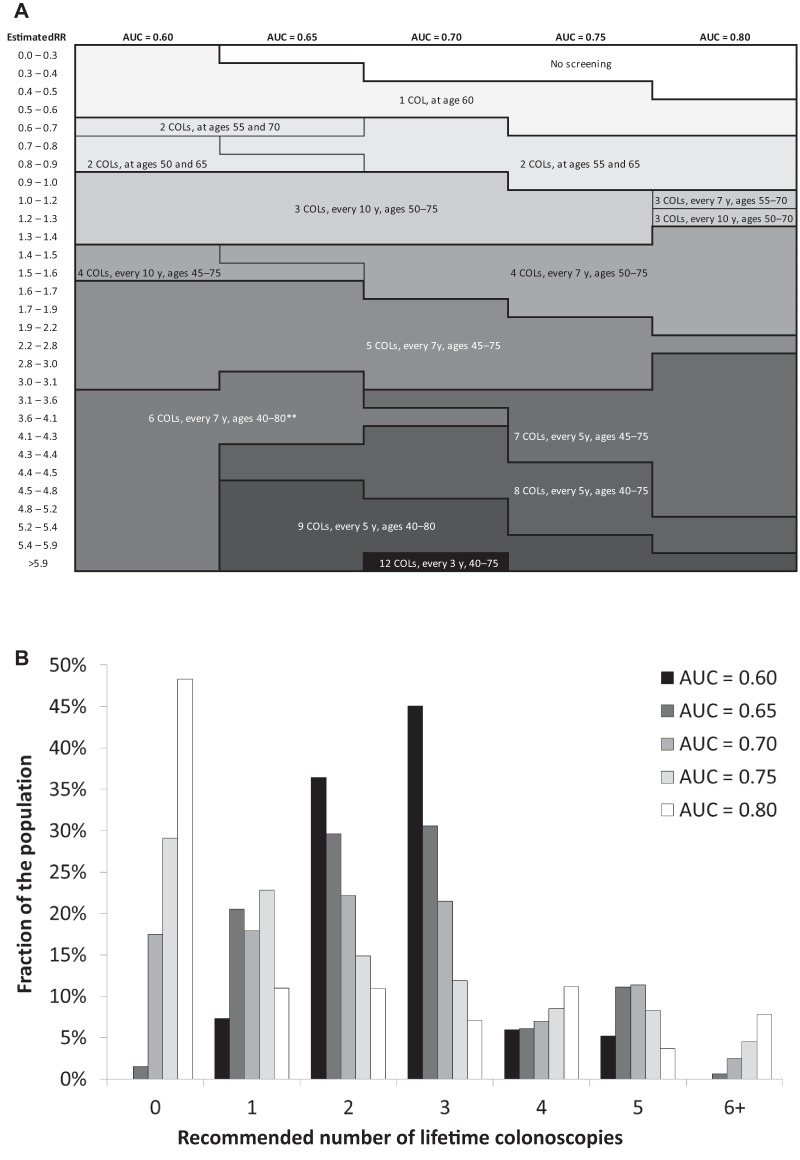
Figure 2.
A) Risk-stratified screening strategies by relative risk (RR) as estimated by a polygenic test with AUC value of 0.60–0.80, given a willingness-to-pay threshold for risk-stratified screening that ensures that the entire risk-stratified screening program yields as least as many QALYs as a uniform screening program with colonoscopies at ages 50, 60, and 70 years.* For every strategy, the number of lifetime colonoscopies, screening interval, and age range of screening is given (ie, “3 COLs, every 10 y, ages 50–75” refers to three lifetime colonoscopies with an interval of 10 years in individuals aged 50–75 years). B) Distribution of recommended numbers of lifetime colonoscopies in the population for different AUC values. RR = relative risk; AUC = area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve; COLs = colonoscopies. *Willingness-to-pay threshold equals $69 000, $65 000, $56 700, $46 000, and $38 500 for AUC = 0.60, 0.65, 0.70, 0.75, and 0.80, respectively. **For AUC = 0.70, individuals with an estimated RR of 3.6–4.1 are offered fewer lifetime screens than those with an estimated RR of 3.1–3.6, but the age range in which they are offered screening is broader.