Figure 6.
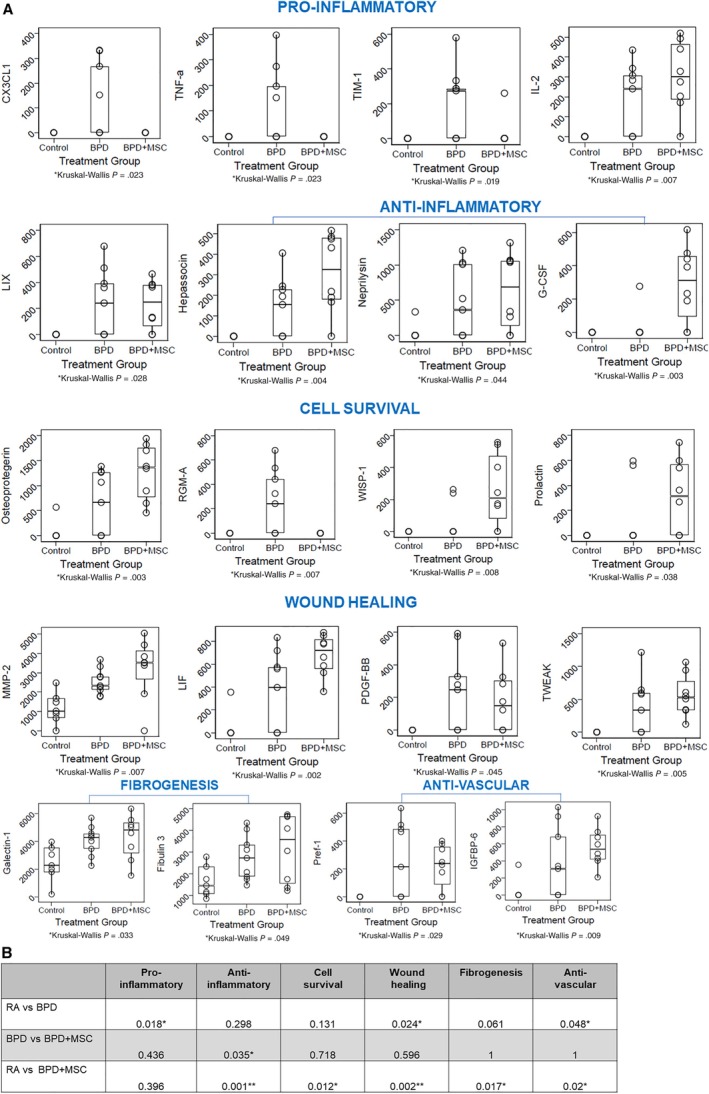
Protein analysis of lung homogenates from room air (RA) control, oxygen injured (bronchopulmonary dysplasia [BPD]), and BPD treated with mesenchymal stromal cells (BPD + MSCs). A, Select data displayed in the following grouping: Pro‐inflammatory; Anti‐inflammatory; Cell survival; Wound healing; Fibrogenesis; and Anti‐vascular. Data presented as mean ± SEM. N, all animals in each group. *P < .05 compared to BPD. CX3CL1, C‐X3‐C motif chemokine ligand 1; G‐CSF, granulocyte colony stimulating factor; IGFBP, insulin like growth factor binding protein; IL, interleukin; LIF, leukemia inhibitory factor; LIX, C‐X‐C motif chemokine 5; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PDGF‐BB, platelet derived growth factor receptor beta; Pref, preadipocyte factor; RGM‐A, repulsive guidance molecule BMP co‐receptor A; TIM, T‐cell immunoglobulin mucin receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis; TWEAK, TNF receptor superfamily member 12A; WISP, WNT1 inducible signaling pathway. B, Mean scores for the cytokines within their respective pathway. Of note, the RA group had multiple pathway differences compared to the other groups. However, only the anti‐inflammatory cytokines yielded significant between the BPD and BPMSC. The groups were examined using ANOVA, followed by pairwise comparisons using Bonferroni's adjusted significance level, where P < .05 was deemed significant
